ANK1 Methylation regulates expression of MicroRNA-486-5p and discriminates lung tumors by histology and smoking status
- PMID: 28965852
- PMCID: PMC5675764
- DOI: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.038
ANK1 Methylation regulates expression of MicroRNA-486-5p and discriminates lung tumors by histology and smoking status
Abstract
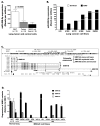
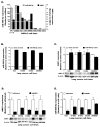
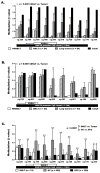
The intragenic tumor-suppressor microRNA miR-486-5p is often down-regulated in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) but the mechanism is unclear. This study investigated epigenetic co-regulation of miR-486-5p and its host gene ANK1. MiR-486-5p expression in lung tumors and cell lines was significantly reduced compared to normal lung (p < 0.001) and is strongly correlated with ANK1 expression. In vitro, siRNA-mediated ANK1 knockdown in NSCLC cells also reduced miR-486-5p while the DNA methylation inhibitor 5-aza-2'-deoxycytidine induced expression of both. ANK1 promoter CpG island was unmethylated in normal lung but methylated in 45% (118/262) lung tumors and 55% (17/31) NSCLC cell lines. After adjustment for tumor histology and smoking, methylation was significantly more prevalent in adenocarcinoma (101/200, 51%) compared to squamous cell carcinoma (17/62, 27%), p < 0.001; HR = 3.513 (CI: 1.818-6.788); and in smokers (73/128, 57%) than never-smokers (28/72, 39%), p = 0.014; HR = 2.086 (CI: 1.157-3.759). These results were independently validated using quantitative methylation data for 809 NSCLC cases from The Cancer Genome Atlas project. Together, our data indicate that aberrant ANK1 methylation is highly prevalent in lung cancer, discriminate tumors by histology and patients' smoking history, and contributes to miR-486-5p repression.
Keywords: ANK1; Epigenetics; Intronic microRNA; NSCLC; miR-486-5p.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Transcriptomic studies provide insights into the tumor suppressive role of miR-146a-5p in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells.RNA Biol. 2019 Dec;16(12):1721-1732. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2019.1657351. Epub 2019 Aug 23. RNA Biol. 2019. PMID: 31425002 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-486-3p functions as a tumor suppressor in oral cancer by targeting DDR1.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019 Jun 28;38(1):281. doi: 10.1186/s13046-019-1283-z. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 31253192 Free PMC article.
-
MiRNA-195-5p Functions as a Tumor Suppressor and a Predictive of Poor Prognosis in Non-small Cell Lung Cancer by Directly Targeting CIAPIN1.Pathol Oncol Res. 2019 Jul;25(3):1181-1190. doi: 10.1007/s12253-018-0552-z. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Pathol Oncol Res. 2019. PMID: 30637589 Free PMC article.
-
Cells of origin of lung cancers: lessons from mouse studies.Genes Dev. 2020 Aug 1;34(15-16):1017-1032. doi: 10.1101/gad.338228.120. Genes Dev. 2020. PMID: 32747478 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Implications of Genomic Discoveries in Lung Cancer.N Engl J Med. 2016 May 12;374(19):1864-73. doi: 10.1056/NEJMra1504688. N Engl J Med. 2016. PMID: 27168435 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
miR-486-5p expression is regulated by DNA methylation in osteosarcoma.BMC Genomics. 2022 Feb 17;23(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s12864-022-08346-6. BMC Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35172717 Free PMC article.
-
MiR-486-5p specifically suppresses SAPCD2 expression, which attenuates the aggressive phenotypes of lung adenocarcinoma cells.Histol Histopathol. 2022 Sep;37(9):909-917. doi: 10.14670/HH-18-463. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Histol Histopathol. 2022. PMID: 35467005
-
miRNA-486-5p: signaling targets and role in non-malignant disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 Jun 22;79(7):376. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04406-y. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35731367 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Could Alzheimer's Disease Originate in the Periphery and If So How So?Mol Neurobiol. 2019 Jan;56(1):406-434. doi: 10.1007/s12035-018-1092-y. Epub 2018 Apr 29. Mol Neurobiol. 2019. PMID: 29705945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-486-5p improves nonsmall-cell lung cancer chemotherapy sensitivity and inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition by targeting twinfilin actin binding protein 1.J Int Med Res. 2019 Aug;47(8):3745-3756. doi: 10.1177/0300060519850739. Epub 2019 May 23. J Int Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31117868 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Tan X, Qin W, Zhang L, Hang J, Li B, Zhang C, Wan J, Zhou F, Shao K, Sun Y, Wu J, Zhang X, Qiu B, Li N, Shi S, Feng X, Zhao S, Wang Z, Zhao X, Chen Z, Mitchelson K, Cheng J, Guo Y, He J. A 5-microRNA signature for lung squamous cell carcinoma diagnosis and hsa-miR-31 for prognosis. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:6802–6811. - PubMed
-
- Oh HK, Tan AL, Das K, Ooi CH, Deng NT, Tan IB, Beillard E, Lee J, Ramnarayanan K, Rha SY, Palanisamy N, Voorhoeve PM, Tan P. Genomic loss of miR-486 regulates tumor progression and the OLFM4 antiapoptotic factor in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:2657–2667. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

