Compulsivity Reveals a Novel Dissociation between Action and Confidence
- PMID: 28965997
- PMCID: PMC5643443
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2017.09.006
Compulsivity Reveals a Novel Dissociation between Action and Confidence
Abstract
Confidence and actions are normally tightly interwoven-if I am sure that it is going to rain, I will take an umbrella-therefore, it is difficult to understand their interplay. Stimulated by the ego-dystonic nature of obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), where compulsive actions are recognized as disproportionate, we hypothesized that action and confidence might be independently updated during learning. Participants completed a predictive-inference task designed to identify how action and confidence evolve in response to surprising changes in the environment. While OCD patients (like controls) correctly updated their confidence according to changes in the environment, their actions (unlike those of controls) mostly disregarded this knowledge. Therefore, OCD patients develop an accurate, internal model of the environment but fail to use it to guide behavior. Results demonstrated a novel dissociation between confidence and action, suggesting a cognitive architecture whereby confidence estimates can accurately track the statistic of the environment independently from performance.
Keywords: action; beliefs; compulsivity; computational psychiatry; confidence; learning; metacognition; obsessive-compulsive disorder; uncertainty.
Copyright © 2017 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
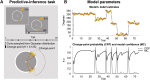
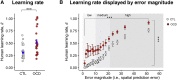
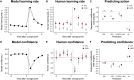

Comment in
-
No confidence in wrong actions.Nat Hum Behav. 2017 Dec;1(12):857. doi: 10.1038/s41562-017-0263-6. Nat Hum Behav. 2017. PMID: 31024177 No abstract available.
References
-
- Behrens T.E.J., Woolrich M.W., Walton M.E., Rushworth M.F.S. Learning the value of information in an uncertain world. Nat. Neurosci. 2007;10:1214–1221. - PubMed
-
- Daw N.D., Niv Y., Dayan P. Uncertainty-based competition between prefrontal and dorsolateral striatal systems for behavioral control. Nat. Neurosci. 2005;8:1704–1711. - PubMed
-
- Denys D., Mantione M., Figee M., van den Munckhof P., Koerselman F., Westenberg H., Bosch A., Schuurman R. Deep brain stimulation of the nucleus accumbens for treatment-refractory obsessive-compulsive disorder. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry. 2010;67:1061–1068. - PubMed
-
- Endrass T., Kloft L., Kaufmann C., Kathmann N. Approach and avoidance learning in obsessive-compulsive disorder. Depress. Anxiety. 2011;28:166–172. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

