Factor XII-Driven Inflammatory Reactions with Implications for Anaphylaxis
- PMID: 28966616
- PMCID: PMC5605561
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01115
Factor XII-Driven Inflammatory Reactions with Implications for Anaphylaxis
Abstract
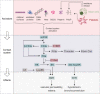
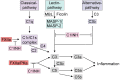
Anaphylaxis is a life-threatening allergic reaction. It is triggered by the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines and mediators from mast cells and basophils in response to immunologic or non-immunologic mechanisms. Mediators that are released upon mast cell activation include the highly sulfated polysaccharide and inorganic polymer heparin and polyphosphate (polyP), respectively. Heparin and polyP supply a negative surface for factor XII (FXII) activation, a serine protease that drives contact system-mediated coagulation and inflammation. Activation of the FXII substrate plasma kallikrein leads to further activation of zymogen FXII and triggers the pro-inflammatory kallikrein-kinin system that results in the release of the mediator bradykinin (BK). The severity of anaphylaxis is correlated with the intensity of contact system activation, the magnitude of mast cell activation, and BK formation. The main inhibitor of the complement system, C1 esterase inhibitor, potently interferes with FXII activity, indicating a meaningful cross-link between complement and kallikrein-kinin systems. Deficiency in a functional C1 esterase inhibitor leads to a severe swelling disorder called hereditary angioedema (HAE). The significance of FXII in these disorders highlights the importance of studying how these processes are integrated and can be therapeutically targeted. In this review, we focus on how FXII integrates with inflammation and the complement system to cause anaphylaxis and HAE as well as highlight current diagnosis and treatments of BK-related diseases.
Keywords: anaphylaxis; bradykinin; contact system; factor XII; heparin; kallikrein–kinin system; mast cells; polyP.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Mast Cell, Contact, and Coagulation System Connection in Anaphylaxis.Front Immunol. 2017 Jul 26;8:846. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.00846. eCollection 2017. Front Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28798744 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pathogenic mechanisms of bradykinin mediated diseases: dysregulation of an innate inflammatory pathway.Adv Immunol. 2014;121:41-89. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00002-7. Adv Immunol. 2014. PMID: 24388213 Review.
-
C1-inhibitor polymers activate the FXII-dependent kallikrein-kinin system: Implication for a role in hereditary angioedema.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1850(6):1336-42. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2015.03.005. Epub 2015 Mar 20. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25800206
-
Plasma contact system activation drives anaphylaxis in severe mast cell-mediated allergic reactions.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 Apr;135(4):1031-1043.e6. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.07.057. Epub 2014 Sep 18. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25240785
-
The factor XIIa blocking antibody 3F7: a safe anticoagulant with anti-inflammatory activities.Ann Transl Med. 2015 Oct;3(17):247. doi: 10.3978/j.issn.2305-5839.2015.09.07. Ann Transl Med. 2015. PMID: 26605293 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Platelets and Immune Responses During Thromboinflammation.Front Immunol. 2019 Jul 26;10:1731. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01731. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31402914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
6-(Arylaminomethyl) Isoquinolines as Enzyme Inhibitors and Their Preparation: A Patent Highlight of Factor XIIa Inhibitors.Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023;21(3):243-249. doi: 10.2174/1871525721666230126114224. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36703578 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of contact-mediated activation of factor XI protects baboons against S aureus-induced organ damage and death.Blood Adv. 2019 Feb 26;3(4):658-669. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2018029983. Blood Adv. 2019. PMID: 30808684 Free PMC article.
-
Pathophysiological, Cellular, and Molecular Events of the Vascular System in Anaphylaxis.Front Immunol. 2022 Mar 8;13:836222. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.836222. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35371072 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanisms Governing Anaphylaxis: Inflammatory Cells, Mediators, Endothelial Gap Junctions and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jul 21;22(15):7785. doi: 10.3390/ijms22157785. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34360549 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

