Protection against Pertussis in Humans Correlates to Elevated Serum Antibodies and Memory B Cells
- PMID: 28966622
- PMCID: PMC5605623
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2017.01158
Protection against Pertussis in Humans Correlates to Elevated Serum Antibodies and Memory B Cells
Abstract
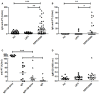
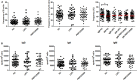
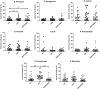
Pertussis is a respiratory infection caused by Bordetella pertussis that may be particularly severe and even lethal in the first months of life when infants are still too young to be vaccinated. Adults and adolescents experience mild symptoms and are the source of infection for neonates. Adoptive maternal immunity does not prevent pertussis in the neonate. We compared the specific immune response of mothers of neonates diagnosed with pertussis and mothers of control children. We show that women have pre-existing pertussis-specific antibodies and memory B cells and react against the infection with a recall response increasing the levels specific serum IgG, milk IgA, and the frequency of memory B cells of all isotypes. Thus, the maternal immune system is activated in response to pertussis and effectively prevents the disease indicating that the low levels of pre-formed serum antibodies are insufficient for protection. For this reason, memory B cells play a major role in the adult defense. The results of this study suggest that new strategies for vaccine design should aim at increasing long-lived plasma cells and their antibodies.
Keywords: immune system; memory B cells; pertussis; sIgA; vaccination.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Identifying long-term memory B-cells in vaccinated children despite waning antibody levels specific for Bordetella pertussis proteins.Vaccine. 2011 Feb 4;29(7):1431-7. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2010.12.033. Epub 2010 Dec 25. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21187178
-
Impact of infant and preschool pertussis vaccinations on memory B-cell responses in children at 4 years of age.Vaccine. 2011 Aug 5;29(34):5725-30. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.05.094. Epub 2011 Jun 12. Vaccine. 2011. PMID: 21669247
-
Kinetics of the antibody response to tetanus-diphtheria-acellular pertussis vaccine in women of childbearing age and postpartum women.Clin Infect Dis. 2011 Nov;53(9):885-92. doi: 10.1093/cid/cir538. Epub 2011 Sep 26. Clin Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21946190 Clinical Trial.
-
Acellular pertussis vaccine use in risk groups (adolescents, pregnant women, newborns and health care workers): a review of evidences and recommendations.Vaccine. 2012 Jul 27;30(35):5179-90. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2012.06.005. Epub 2012 Jun 15. Vaccine. 2012. PMID: 22709953 Review.
-
Waning and aging of cellular immunity to Bordetella pertussis.Pathog Dis. 2015 Nov;73(8):ftv071. doi: 10.1093/femspd/ftv071. Epub 2015 Sep 13. Pathog Dis. 2015. PMID: 26371178 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibody persistence 2 and 3 years after booster vaccination of adolescents with recombinant acellular pertussis monovalent aPgen or combined TdaPgen vaccines.EClinicalMedicine. 2021 Jun 23;37:100976. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.100976. eCollection 2021 Jul. EClinicalMedicine. 2021. PMID: 34386749 Free PMC article.
-
Antibody Response to Pertussis Vaccination in Pregnant and Non-Pregnant Women-The Role of Sex Hormones.Vaccines (Basel). 2021 Jun 10;9(6):637. doi: 10.3390/vaccines9060637. Vaccines (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34200795 Free PMC article.
-
Immunization with whole cell but not acellular pertussis vaccines primes CD4 TRM cells that sustain protective immunity against nasal colonization with Bordetella pertussis.Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019;8(1):169-185. doi: 10.1080/22221751.2018.1564630. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2019. PMID: 30866771 Free PMC article.
-
Vaccination against Paediatric Respiratory Pathogens.Vaccines (Basel). 2019 Nov 1;7(4):168. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7040168. Vaccines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31683882 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Long-Term Analysis of Pertussis Vaccine Immunity to Identify Potential Markers of Vaccine-Induced Memory Associated With Whole Cell But Not Acellular Pertussis Immunization in Mice.Front Immunol. 2022 Feb 8;13:838504. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.838504. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35211125 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lönnerdal B. Nutritional and physiologic significance of human milk proteins. Am J Clin Nutr (2003) 77:1537S–43S. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

