Dried Rehmannia root protects against glutamate-induced cytotoxity to PC12 cells through energy metabolism-related pathways
- PMID: 28966650
- PMCID: PMC5607830
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.213556
Dried Rehmannia root protects against glutamate-induced cytotoxity to PC12 cells through energy metabolism-related pathways
Abstract
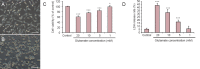
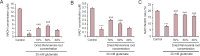
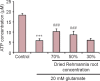
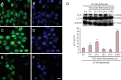
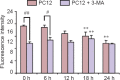
Rehmannia has been shown to be clinically effective in treating neurodegenerative diseases; however, the neuroprotective mechanisms remain unclear. In this study, we established a model of neurodegenerative disease using PC12 cytotoxic injury induced by glutamate. The cells were treated with 20 mM glutamate in the absence or presence of water extracts of dried Rehmannia root of varying concentrations (70%, 50% and 30%). The different concentrations of Rehmannia water extract significantly increased the activity of glutamate-injured cells, reduced the release of lactate dehydrogenase, inhibited apoptosis, increased the concentrations of NADH, NAD and ATP in cells, ameliorated mitochondrial membrane potential, and reduced the levels of light chain 3. Taken together, our findings demonstrate that Rehmannia water extracts exert a cytoprotective effect against glutamate-induced PC12 cell injury via energy metabolism-related pathways.
Keywords: PC12 cells; Rehmannia water extracts; autophagy; energy metabolism; glutamate; nerve regeneration; neural regeneration.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest: None declared.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Protective effect of 7-difluoromethoxy-5,4'-Di-hydroxyl isoflavone against the damage induced by glutamate in PC12 cells.Int J Mol Med. 2012 Nov;30(5):1159-65. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2012.1109. Epub 2012 Aug 23. Int J Mol Med. 2012. PMID: 22922702
-
Neuroprotective effect of water extract of Panax ginseng on corticosterone-induced apoptosis in PC12 cells and its underlying molecule mechanisms.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Jan 15;159:102-12. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.10.062. Epub 2014 Nov 15. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25446601
-
Protective effects of organic extracts of Alpinia oxyphylla against hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity in PC12 cells.Neural Regen Res. 2020 Apr;15(4):682-689. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.266918. Neural Regen Res. 2020. PMID: 31638092 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroprotective effects of 20(S)-protopanaxadiol against glutamate-induced mitochondrial dysfunction in PC12 cells.Int J Mol Med. 2016 Feb;37(2):378-86. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2015.2440. Epub 2015 Dec 21. Int J Mol Med. 2016. PMID: 26709399 Free PMC article.
-
FAM3A Protects Against Glutamate-Induced Toxicity by Preserving Calcium Homeostasis in Differentiated PC12 Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017;44(5):2029-2041. doi: 10.1159/000485943. Epub 2017 Dec 12. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2017. PMID: 29241198
Cited by
-
Moschus ameliorates glutamate-induced cellular damage by regulating autophagy and apoptosis pathway.Sci Rep. 2023 Oct 30;13(1):18586. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-45878-7. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37903904 Free PMC article.
-
Sulforaphane prevents PC12 cells from oxidative damage via the Nrf2 pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2019 Jun;19(6):4890-4896. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2019.10148. Epub 2019 Apr 10. Mol Med Rep. 2019. PMID: 31059012 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine Attenuates Glutamate-Induced Cytotoxicity by Inhibiting the Mitochondrial-Mediated Apoptotic Pathway.Med Sci Monit. 2020 May 18;26:e922139. doi: 10.12659/MSM.922139. Med Sci Monit. 2020. PMID: 32419697 Free PMC article.
-
The efficacy and safety of Chinese herbal medicine as an add-on therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.Front Neurol. 2022 Oct 6;13:988034. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.988034. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36277914 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Brittain JM, Chen L, Wilson SM, Brustovetsky T, Gao X, Ashpole NM, Molosh AI, You H, Hudmon A, Shekhar A, White FA, Zamponi GW, Brustovetsky N, Chen J, Khanna R. Neuroprotection against traumatic brain injury by a peptide derived from the collapsin response mediator protein 2 (CRMP2) J Biol Chem. 2011;286:37778–37792. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Capaldi RA, Aggeler R, Turina P, Wilkens S. Coupling between catalytic sites and the proton channel in F1F0-type ATPases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994;19:284–289. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

