Silencing of α-complex protein-2 reverses alcohol- and cytokine-induced fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells
- PMID: 28966795
- PMCID: PMC5613955
- DOI: 10.1016/j.livres.2017.05.003
Silencing of α-complex protein-2 reverses alcohol- and cytokine-induced fibrogenesis in hepatic stellate cells
Abstract
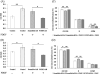
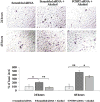
Background and aim: α-complex protein-2 (αCP2) encoded by the poly (rC) binding protein 2(PCBP2) gene is responsible for the accumulation of type I collagen in fibrotic livers. In this study, we silenced the PCBP2 gene using a small interfering RNA (siRNA) to reverse alcohol-and cytokine-induced profibrogenic effects on hepatic stellate cells (HSCs).
Methods: Primary rat HSCs and the HSC-T6 cell line were used as fibrogenic models to mimic the initiation and perpetuation stages of fibrogenesis, respectively. We previously found that a PCBP2 siRNA, which efficiently silences expression of αCP2, reduces the stability of type I collagen mRNA. We investigated the effects of the PCBP2 siRNA on cell proliferation and migration. Expression of type I collagen in HSCs was analyzed by quantitative real-time PCR and western blotting. In addition, we evaluated the effects of the PCBP2 siRNA on apoptosis and the cell cycle.
Results: PCBP2 siRNA reversed multiple alcohol- and cytokine-induced profibrogenic effects on primary rat HSCs and HSC-T6 cells. The PCBP2 siRNA also reversed alcohol- and cytokine-induced accumulation of type I collagen as well as cell proliferation and migration. Moreover, the combination of LY2109761, a transforming growth factor-β1 inhibitor, and the PCBP2 siRNA exerted a synergistic inhibitive effect on the accumulation of type I collagen in HSCs.
Conclusions: Silencing of PCBP2 using siRNA could be a potential therapeutic strategy for alcoholic liver fibrosis.
Keywords: Epidermal growth factor (EGF); Hepatic stellate cells; LY2a09761; Liver fibrosis; Migration; Myofibroblast; Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF); Poly (rC) binding protein (PCBP)2; Primary HSC; Transforming growth factor (TGF)-β.
Figures
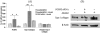





References
-
- Friedman SL. Liver fibrosis -- from bench to bedside. J Hepatol. 2003;38(Suppl 1):S38–S53. - PubMed
-
- Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL. Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2011;6:425–456. - PubMed
-
- Friedman SL. Evolving challenges in hepatic fibrosis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2010;7:425–436. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
