Purifying Properly Folded Cysteine-rich, Zinc Finger Containing Recombinant Proteins for Structural Drug Targeting Studies: the CH1 Domain of p300 as a Case Example
- PMID: 28966947
- PMCID: PMC5621770
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2537
Purifying Properly Folded Cysteine-rich, Zinc Finger Containing Recombinant Proteins for Structural Drug Targeting Studies: the CH1 Domain of p300 as a Case Example
Abstract
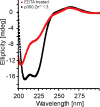
The transcription factor Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF) complexes with the coactivator p300, activating the hypoxia response pathway and allowing tumors to grow. The CH1 and CAD domains of each respective protein form the interface between p300 and HIF. Small molecule compounds are in development that target and inhibit HIF/p300 complex formation, with the goal of reducing tumor growth. High resolution NMR spectroscopy is necessary to study ligand interaction with p300-CH1, and purifying high quantities of properly folded p300-CH1 is needed for pursuing structural and biophysical studies. p300-CH1 has 3 zinc fingers and 9 cysteine residues, posing challenges associated with reagent compatibility and protein oxidation. A protocol has been developed to overcome such issues by incorporating zinc during expression and streamlining the purification time, resulting in a high yield of optimally folded protein (120 mg per 4 L expression media) that is suitable for structural NMR studies. The structural integrity of the final recombinant p300-CH1 has been verified to be optimal using onedimensional 1H NMR spectroscopy and circular dichroism. This protocol is applicable for the purification of other zinc finger containing proteins.
Keywords: CBP; CH1; Cysteine; HIF; Hypoxia; Recombinant protein purification; Zinc finger; p300.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Structural basis for negative regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha by CITED2.Nat Struct Biol. 2003 Jul;10(7):504-12. doi: 10.1038/nsb936. Nat Struct Biol. 2003. PMID: 12778114
-
Three conformational states of the p300 CH1 domain define its functional properties.Biochemistry. 2003 Aug 26;42(33):9937-45. doi: 10.1021/bi034989o. Biochemistry. 2003. PMID: 12924942
-
Complex regulation of the transactivation function of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha by direct interaction with two distinct domains of the CREB-binding protein/p300.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 22;285(4):2601-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.021824. Epub 2009 Oct 30. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19880525 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Discovery of HIF-1α-p300/CBP Inhibitors as Anti-Cancer Agents.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018;18(4):296-309. doi: 10.2174/1389557516666160630124938. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 27484627 Review.
-
CITED2 and the modulation of the hypoxic response in cancer.World J Clin Oncol. 2020 May 24;11(5):260-274. doi: 10.5306/wjco.v11.i5.260. World J Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32728529 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Zinc finger structure determination by NMR: Why zinc fingers can be a handful.Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2022 Jun-Aug;130-131:62-105. doi: 10.1016/j.pnmrs.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 15. Prog Nucl Magn Reson Spectrosc. 2022. PMID: 36113918 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belozerov VE, Van Meir EG. Inhibitors of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 signaling. Curr Opin Investig Drugs. 2006;7(12):1067–1076. - PubMed
-
- Brat DJ, Van Meir EG. Vaso-occlusive and prothrombotic mechanisms associated with tumor hypoxia, necrosis, and accelerated growth in glioblastoma. Lab Invest. 2004;84(4):397–405. - PubMed
-
- De Guzman RN, Wojciak JM, Martinez-Yamout MA, Dyson HJ, Wright PE. CBP/p300 TAZ1 domain forms a structured scaffold for ligand binding. Biochemistry. 2005;44(2):490–497. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

