Adjuvant Sunitinib for High-risk Renal Cell Carcinoma After Nephrectomy: Subgroup Analyses and Updated Overall Survival Results
- PMID: 28967554
- PMCID: PMC6684251
- DOI: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.008
Adjuvant Sunitinib for High-risk Renal Cell Carcinoma After Nephrectomy: Subgroup Analyses and Updated Overall Survival Results
Abstract
Background: Adjuvant sunitinib significantly improved disease-free survival (DFS) versus placebo in patients with locoregional renal cell carcinoma (RCC) at high risk of recurrence after nephrectomy (hazard ratio [HR] 0.76, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.59-0.98; p=0.03).
Objective: To report the relationship between baseline factors and DFS, pattern of recurrence, and updated overall survival (OS).
Design, setting, and participants: Data for 615 patients randomized to sunitinib (n=309) or placebo (n=306) in the S-TRAC trial.
Outcome measurements and statistical analysis: Subgroup DFS analyses by baseline risk factors were conducted using a Cox proportional hazards model. Baseline risk factors included: modified University of California Los Angeles integrated staging system criteria, age, gender, Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group performance status (ECOG PS), weight, neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and Fuhrman grade.
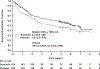
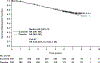
Results and limitations: Of 615 patients, 97 and 122 in the sunitinib and placebo arms developed metastatic disease, with the most common sites of distant recurrence being lung (40 and 49), lymph node (21 and 26), and liver (11 and 14), respectively. A benefit of adjuvant sunitinib over placebo was observed across subgroups, including: higher risk (T3, no or undetermined nodal involvement, Fuhrman grade ≥2, ECOG PS ≥1, T4 and/or nodal involvement; hazard ratio [HR] 0.74, 95% confidence interval [CI] 0.55-0.99; p=0.04), NLR ≤3 (HR 0.72, 95% CI 0.54-0.95; p=0.02), and Fuhrman grade 3/4 (HR 0.73, 95% CI 0.55-0.98; p=0.04). All subgroup analyses were exploratory, and no adjustments for multiplicity were made. Median OS was not reached in either arm (HR 0.92, 95% CI 0.66-1.28; p=0.6); 67 and 74 patients died in the sunitinib and placebo arms, respectively.
Conclusions: A benefit of adjuvant sunitinib over placebo was observed across subgroups. The results are consistent with the primary analysis, which showed a benefit for adjuvant sunitinib in patients at high risk of recurrent RCC after nephrectomy.
Patient summary: Most subgroups of patients at high risk of recurrent renal cell carcinoma after nephrectomy experienced a clinical benefit with adjuvant sunitinib.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00375674.
Keywords: Adjuvant; Disease-free survival; Renal cell carcinoma; Sunitinib.
Copyright © 2017 European Association of Urology. Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Are We Ready for Adjuvant Sunitinib in High-risk Renal Cell Carcinoma?Eur Urol. 2018 Jan;73(1):69-70. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2017.09.026. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Eur Urol. 2018. PMID: 29032154 No abstract available.
References
-
- National Cancer Institute. SEER cancer statistics factsheets: kidney and renal pelvis cancer 2016. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/kidrp.html
-
- Janzen NK, Kim HL, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Surveillance after radical or partial nephrectomy for localized renal cell carcinoma and management of recurrent disease. Urol Clin North Am 2003;30:843–52. - PubMed
-
- Ravaud A, Motzer RJ, Pandha HS, et al. Adjuvant sunitinib in high-risk renal-cell carcinoma after nephrectomy. N Engl J Med 2016;375:2246–54. - PubMed
-
- Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Dorey F, et al. Improved prognostication of renal cell carcinoma using an integrated staging system. J Clin Oncol 2001;19:1649–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

