Adhesion G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Drug Targets
- PMID: 28968187
- PMCID: PMC7167285
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-010617-052933
Adhesion G Protein-Coupled Receptors as Drug Targets
Abstract
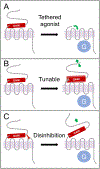
The adhesion G protein-coupled receptors (aGPCRs) are an evolutionarily ancient family of receptors that play key roles in many different physiological processes. These receptors are notable for their exceptionally long ectodomains, which span several hundred to several thousand amino acids and contain various adhesion-related domains, as well as a GPCR autoproteolysis-inducing (GAIN) domain. The GAIN domain is conserved throughout almost the entire family and undergoes autoproteolysis to cleave the receptors into two noncovalently-associated protomers. Recent studies have revealed that the signaling activity of aGPCRs is largely determined by changes in the interactions among these protomers. We review recent advances in understanding aGPCR activation mechanisms and discuss the physiological roles and pharmacological properties of aGPCRs, with an eye toward the potential utility of these receptors as drug targets.
Keywords: agonist; antagonist; antibody; ligand; pharmaceutical; therapeutic.
Figures


References
-
- Baud V, Chissoe SL, Viegas-Pequignot E, Diriong S, N’Guyen VC, et al. 1995. EMR1, an unusual member in the family of hormone receptors with seven transmembrane segments. Genomics 26:334–44 - PubMed
-
- Hamann J, Eichler W, Hamann D, Kerstens HM, Poddighe PJ, et al. 1995. Expression cloning and chromosomal mapping of the leukocyte activation antigen CD97, a new seven-span transmembrane molecule of the secretion receptor superfamily with an unusual extracellular domain. J Immunol 155:1942–50 - PubMed
-
- Stacey M, Lin HH, Gordon S, McKnight AJ. 2000. LNB-TM7, a group of seven-transmembrane proteins related to family-B G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Biochem Sci 25:284–9 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

