Effects of glutamate and ivermectin on single glutamate-gated chloride channels of the parasitic nematode H. contortus
- PMID: 28968469
- PMCID: PMC5638611
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006663
Effects of glutamate and ivermectin on single glutamate-gated chloride channels of the parasitic nematode H. contortus
Abstract
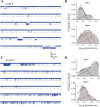
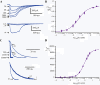
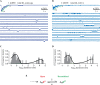
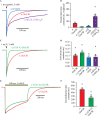
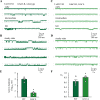
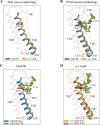
Ivermectin (IVM) is a widely-used anthelmintic that works by binding to and activating glutamate-gated chloride channel receptors (GluClRs) in nematodes. The resulting chloride flux inhibits the pharyngeal muscle cells and motor neurons of nematodes, causing death by paralysis or starvation. IVM resistance is an emerging problem in many pest species, necessitating the development of novel drugs. However, drug optimisation requires a quantitative understanding of GluClR activation and modulation mechanisms. Here we investigated the biophysical properties of homomeric α (avr-14b) GluClRs from the parasitic nematode, H. contortus, in the presence of glutamate and IVM. The receptor proved to be highly responsive to low nanomolar concentrations of both compounds. Analysis of single receptor activations demonstrated that the GluClR oscillates between multiple functional states upon the binding of either ligand. The G36'A mutation in the third transmembrane domain, which was previously thought to hinder access of IVM to its binding site, was found to decrease the duration of active periods and increase receptor desensitisation. On an ensemble macropatch level the mutation gave rise to enhanced current decay and desensitisation rates. Because these responses were common to both glutamate and IVM, and were observed under conditions where agonist binding sites were likely saturated, we infer that G36'A affects the intrinsic properties of the receptor with no specific effect on IVM binding mechanisms. These unexpected results provide new insights into the activation and modulatory mechanisms of the H. contortus GluClRs and provide a mechanistic framework upon which the actions of drugs can be reliably interpreted.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures





References
-
- Gration KA, Clark RB, Usherwood PN. Three types of L-glutamate receptor on junctional membrane of locust muscle fibres. Brain research. 1979;171(2):360–4. Epub 1979/08/03. . - PubMed
-
- Wolstenholme AJ. Glutamate-gated chloride channels. The Journal of biological chemistry. 2012;287(48):40232–8. Epub 2012/10/06. doi: 10.1074/jbc.R112.406280 ; PubMed Central PMCID: PMC3504739. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cully DF, Vassilatis DK, Liu KK, Paress PS, Van der Ploeg LH, Schaeffer JM, et al. Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1994;371(6499):707–11. Epub 1994/10/20. doi: 10.1038/371707a0 . - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

