52-week results of the phase 3 randomized study comparing SB4 with reference etanercept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 28968793
- PMCID: PMC5850652
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kex269
52-week results of the phase 3 randomized study comparing SB4 with reference etanercept in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
Objective: To compare the 52-week efficacy and safety of SB4 [an etanercept biosimilar] with reference etanercept (ETN) in patients with active RA.
Methods: In a phase 3, randomized, double-blind, multicentre study, patients with moderate to severe RA despite MTX treatment were randomized to receive 50 mg/week of s.c. SB4 or ETN up to week 52. Efficacy assessments included ACR response rates, 28-joint DAS, Simplified and Clinical Disease Activity Indices and changes in the modified total Sharp score (mTSS). Safety and immunogenicity were also evaluated.
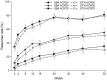
Results: A total of 596 patients were randomized to receive either SB4 (n = 299) or ETN (n = 297) and 505 (84.7%) patients completed 52 weeks of the study. At week 52, the ACR20 response rates in the per-protocol set were comparable between SB4 (80.8%) and ETN (81.5%). All efficacy results were comparable between the two groups and they were maintained up to week 52. Radiographic progression was also comparable and the change from baseline in the mTSS was 0.45 for SB4 and 0.74 for ETN. The safety profile of SB4 was similar to that of ETN and the incidence of anti-drug antibody development up to week 52 was 1.0 and 13.2% in the SB4 and ETN groups, respectively.
Conclusion: Efficacy including radiographic progression was comparable between SB4 and ETN up to week 52. SB4 was well tolerated and had a similar safety profile to that of ETN.
Trial registration number: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01895309, EudraCT 2012-005026-30.
Keywords: Benepali; SB4; biologics; biosimilar; etanercept; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology. All rights reserved. For Permissions, please email: journals.permissions@oup.com
Figures


References
-
- Ruff L, Rezk MF, Uhlig T, Gommers JW.. Budget impact analysis of an etanercept biosimilar for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis in Europe. Value Health 2015;18:A639.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

