Predictive single nucleotide polymorphism markers for acute oral mucositis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with radiotherapy
- PMID: 28968968
- PMCID: PMC5609900
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18450
Predictive single nucleotide polymorphism markers for acute oral mucositis in patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with radiotherapy
Abstract
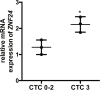
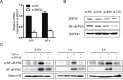
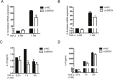
The aim of this study was to investigate the association between the susceptibility of severe oral mucositis (OM) in Chinese nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) patients treated with radiotherapy and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) across the whole genome. SNPs were screened in a total of 24 patients with NPC and an additional 6 were subjected to mRNA expression analysis. Patients were subdivided into CTC 0-2 (CTC toxicity grade 0, 1, and 2) and CTC 3+ (CTC toxicity grade 3 and above) groups according to their CTC (common toxicity criteria) scores. The GTEx dataset was used to performed eQTL analyses and in-vitro functional assays were performed for eQTL-associated genes. Our data identified 7 functional SNPs associated with the development of OM. We observed that rs11081899-A, located in the 5'-UTR of the ZNF24 gene, was significantly correlated with a higher risk of severe mucositis (OR = 14.631, 95% CI = 2.61-105.46, p = 1.2 × 10-4), and positively associated with ZNF24 mRNA expression (p = 4.1 × 10-6) from GTEx dataset. In addition, high ZNF24 mRNA expression was associated with severe OM in patients with NPC (p = 0.02). Further functional assays revealed that ZNF24 knockdown reduced p65 expression and suppressed TNF-α-induced NF-κB activation and pro-inflammatory cytokines release. These findings suggested that rs11081899-A may be a genetic susceptibility factor for radiation-induced OM in patients with NPC, although its value in clinical application needs to be further verified in a large cohort. Also, we suggested that downregulation of ZNF24 may attenuate the development of mucositis by suppressing NF-κB activation.
Keywords: ZNF24; genetic polymorphism; nasopharyngeal carcinoma; oral mucositis; radiotherapy.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acute oral mucositis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma patients treated with radiotherapy: association with genetic polymorphism in DNA DSB repair genes.Int J Radiat Biol. 2014 Mar;90(3):256-61. doi: 10.3109/09553002.2014.873558. Epub 2014 Jan 24. Int J Radiat Biol. 2014. PMID: 24350917
-
Genome-wide association study identifies genetic susceptibility loci and pathways of radiation-induced acute oral mucositis.J Transl Med. 2020 Jun 5;18(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s12967-020-02390-0. J Transl Med. 2020. PMID: 32503578 Free PMC article.
-
[Clinical study in prophylactic use of chinese medicine to prevent chemoradiotherapy induced mucositis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma].Ai Zheng. 2003 Oct;22(10):1084-7. Ai Zheng. 2003. PMID: 14558957 Clinical Trial. Chinese.
-
Single Nucleotide Polymorphisms as Biomarker Predictors of Oral Mucositis Severity in Head and Neck Cancer Patients Submitted to Combined Radiation Therapy and Chemotherapy: A Systematic Review.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Feb 27;16(5):949. doi: 10.3390/cancers16050949. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38473311 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive intervention possibilities in radiotherapy- and chemotherapy-induced oral mucositis: results of meta-analyses.J Dent Res. 2006 Aug;85(8):690-700. doi: 10.1177/154405910608500802. J Dent Res. 2006. PMID: 16861284 Review.
Cited by
-
Genetic polymorphisms of genes involved in oxidative stress and inflammatory management in oncopediatric patients with chemo-induced oral mucositis.J Appl Oral Sci. 2022 Mar 23;30:e20210490. doi: 10.1590/1678-7757-2021-0490. eCollection 2022. J Appl Oral Sci. 2022. PMID: 35319668 Free PMC article.
-
Prediction of mucositis risk secondary to cancer therapy: a systematic review of current evidence and call to action.Support Care Cancer. 2020 Nov;28(11):5059-5073. doi: 10.1007/s00520-020-05579-7. Epub 2020 Jun 26. Support Care Cancer. 2020. PMID: 32592033
-
Polymorphism of regulatory region of APEH gene (c.-521G>C, rs4855883) as a relevant predictive factor for radiotherapy induced oral mucositis and overall survival in head neck cancer patients.Oncotarget. 2018 Jul 3;9(51):29644-29653. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25662. eCollection 2018 Jul 3. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30038710 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Mammalian Target of Rapamycin (mTOR) in Pulmonary Fibrosis.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Mar 8;19(3):778. doi: 10.3390/ijms19030778. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 29518028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Research status and prospects of biomarkers for nasopharyngeal carcinoma in the era of high‑throughput omics (Review).Int J Oncol. 2021 Apr;58(4):9. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2021.5188. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Int J Oncol. 2021. PMID: 33649830 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chang ET, Adami HO. The enigmatic epidemiology of nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2006;15:1765–77. - PubMed
-
- Ou X, Zhou X, Shi Q, Xing X, Yang Y, Xu T, Shen C, Wang X, He X, Kong L, Ying H, Hu C. Treatment outcomes and late toxicities of 869 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with definitive intensity modulated radiation therapy: new insight into the value of total dose of cisplatin and radiation boost. Oncotarget. 2015;6:38381–97. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5420. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhao C, Xiao WW, Han F, Lu LX, Wu SX, Chen JZ, Lin CG, Huang SM, Deng XW, Lu TX, Cui NJ. Long-term outcome and prognostic factors of patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma treated with intensity-modulated radiation therapy. Chin J Radiat Oncol. 2010;19:191–196.
-
- Sun X, Su S, Chen C, Han F, Zhao C, Xiao W, Deng X, Huang S, Lin C, Lu T. Long-term outcomes of intensity- modulated radiotherapy for 868 patients with nasopharyngeal carcinoma: an analysis of survival and treatment toxicities. Radiother Oncol. 2014;110:398–403. - PubMed
-
- Chua ML, Wee JT, Hui EP, Chan AT. Nasopharyngeal carcinoma. Lancet. 2016;387:1012–24. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

