Similar outcomes after haploidentical transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide versus HLA-matched transplantation: a meta-analysis of case-control studies
- PMID: 28969012
- PMCID: PMC5609944
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.18862
Similar outcomes after haploidentical transplantation with post-transplant cyclophosphamide versus HLA-matched transplantation: a meta-analysis of case-control studies
Abstract
Background: Outcomes of haploidentical hematopoietic cell transplantation (haplo-HCT) with post-transplant cyclophosphamide (PT-Cy) have greatly improved. It remains unknown whether haplo-HCT with PT-Cy was associated with poor outcomes when compared with HLA-matched HCT. To address this issue, we performed a meta-analysis to compare outcomes of haplo-HCT with PT-Cy with those of HLA-matched HCT.
Methods: A systematic search for case-control studies were performed in PubMed, Embase and Cochrane Library databases. Using a random model, the risk ratios (RRs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CI) were pooled for the final analysis.
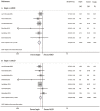
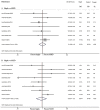
Results: Nine case-control studies including 2258 patients (827 patients in the haplo-HCT with PT-Cy group, 748 controls from HLA-matched related donors (MRD), and 683 controls from HLA-matched unrelated donors (MUD)) met the inclusion criteria. No differences were found between haplo-HCT with PT-Cy and HLA-matched HCT with regard to acute graft-versus-host-disease (GVHD), non-relapse mortality, relapse, progression free survival and overall survival. However, haplo-HCT with PT-Cy was found to be associated with a lower incidence of moderate to severe chronic GVHD (Haplo vs MRD: RR=0.54; 95% CI=0.39-0.75; Haplo vs MUD: RR=0.70; 95% CI=0.56-0.88).
Conclusions: The results of this meta-analysis suggest that haplo-HCT with PT-Cy can achieve comparable outcomes with those of HLA-matched HCT. Haploidentical donors can be a feasible and valid alternative when conventional HLA-matched donors are unavailable.
Keywords: HLA-matched; haploidentical; hematopoietic cell transplantation; post-transplant cyclophosphamide; similar outcomes.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST The authors declare that they have no competing interests
Figures





References
-
- Beatty PG, Clift RA, Mickelson EM, Nisperos BB, Flournoy N, Martin PJ, Sanders JE, Stewart P, Buckner CD, Storb R, Thomas D, Hansen JA. Marrow transplantation from related donors other than HLA-identical siblings. N Engl J Med. 1985;313:765–771. - PubMed
-
- Szydlo R, Goldman JM, Klein JP, Gale RP, Ash RC, Bach FH, Bradley BA, Casper JT, Flomenberg N, Gajewski JL, Gluckman E, Henslee-Downey PJ, Hows JM, et al. Results of allogeneic bone marrow transplants for leukemia using donors other than HLA-identical siblings. J Clin Oncol. 1997;15:1767–1777. - PubMed
-
- Henslee-Downey PJ, Parrish RS, MacDonald JS, Romond EH, Marciniak E, Coffey C, Ciocci G, Thompson JS. Combined in vitro and in vivo T lymphocyte depletion for the control of graft-versus-host disease following haploidentical marrow transplant. Transplantation. 1996;61:738–745. - PubMed
-
- Aversa F, Tabilio A, Velardi A, Cunningham I, Terenzi A, Falzetti F, Ruggeri L, Barbabietola G, Aristei C, Latini P, Reisner Y, Martelli MF. Treatment of high-risk acute leukemia with T-cell-depleted stem cells from related donors with one fully mismatched HLA haplotype. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:1186–1193. - PubMed
-
- Lu DP, Dong L, Wu T, Huang XJ, Zhang MJ, Han W, Chen H, Liu DH, Gao ZY, Chen YH, Xu LP, Zhang YC, Ren HY, et al. Conditioning including antithymocyte globulin followed by unmanipulated HLA-mismatched/haploidentical blood and marrow transplantation can achieve comparable outcomes with HLA-identical sibling transplantation. Blood. 2006;107:3065–3073. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

