Day/Night and Summer/Winter Changes in Serum Total Antioxidant Capacity
- PMID: 28969574
- PMCID: PMC5907061
- DOI: 10.2174/1573406413666171002123158
Day/Night and Summer/Winter Changes in Serum Total Antioxidant Capacity
Abstract
Background: Seasonal and circadian changes are two factors described to affect blood levels of some biological molecules. The Total Antioxidant Capacity (TAC) is one global measure of the antioxidant capacity of a system. There is no agreement about the existence of day/night changes in TAC levels as well as there is no information about seasonal changes in TAC levels.
Objective: The aims of this research are studying if there are summer/winter changes in TAC concentrations or if TAC concentrations have day/night changes.
Method: Ninety-eight healthy subjects took part in the summer study of whom 64 participated in the winter one. Blood was sampled at 09:00, 12:00 and 00:00 h. TAC was measured by the ABTS radical cation technique. Results are expressed in mmol/L of trolox equivalents.
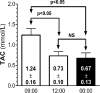
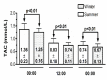
Results: The subjects had significantly higher TAC levels in summer than winter at the three-time point studied. Summer 09:00 TAC concentration was significantly higher than the 12:00 and 00:00 h concentrations (1.34±0.26 vs 0.83±0.19, 0.75±0.18). Summer TAC 12:00 h concentrations were significantly higher than the 00:00 h concentrations (0.83±0.19 vs. 0.75±0.18). Winter 09:00 TAC concentrations were significantly higher than the 12:00 and 00:00 h concentrations (1.24±0.16 vs. 0.73±0.10, 0.67±0.13). There were no significant differences between the 12:00 and 00:00 h TAC concentrations.
Conclusion: Strong methodological biases may be made if the seasonal and circadian changes in serum TAC concentration are not taken into account when researching in this area.
Keywords: Antioxidants; biological variation; circadian rhythms; methodology; seasonal rhythms; total antioxidant capacity.
Copyright© Bentham Science Publishers; For any queries, please email at epub@benthamscience.org.
Figures

References
-
- Klerman E.B., Gershengorn H.B., Duffy J.F., Kronauer R.E. Comparisons of the variability of three markers of the human circadian pacemaker. J. Biol. Rhythms. 2002;17:181–193. - PubMed
-
- Morera A.L., Abreu P. Daytime/night-time and summer/winter melatonin and malondialdehyde rhythms: An inverse relationship. J. Pineal Res. 2007;43:313–314. - PubMed
-
- Morera A.L., Abreu P. Seasonality of psychopathology and circannual melatonin rhythm. J. Pineal Res. 2006;41:279–283. - PubMed
-
- Morera-Fumero A.L., Abreu-Gonzalez P., Henry-Benitez M., Yelmo-Cruz S., Diaz-Mesa E. Summer/winter changes in serum s100b protein concentration as a source of research variance. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013;47:791–795. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

