SimBA: A methodology and tools for evaluating the performance of RNA-Seq bioinformatic pipelines
- PMID: 28969586
- PMCID: PMC5623974
- DOI: 10.1186/s12859-017-1831-5
SimBA: A methodology and tools for evaluating the performance of RNA-Seq bioinformatic pipelines
Abstract
Background: The evolution of next-generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has led to increased focus on RNA-Seq. Many bioinformatic tools have been developed for RNA-Seq analysis, each with unique performance characteristics and configuration parameters. Users face an increasingly complex task in understanding which bioinformatic tools are best for their specific needs and how they should be configured. In order to provide some answers to these questions, we investigate the performance of leading bioinformatic tools designed for RNA-Seq analysis and propose a methodology for systematic evaluation and comparison of performance to help users make well informed choices.
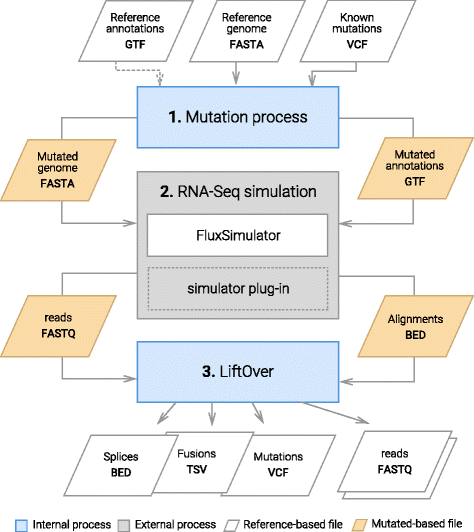
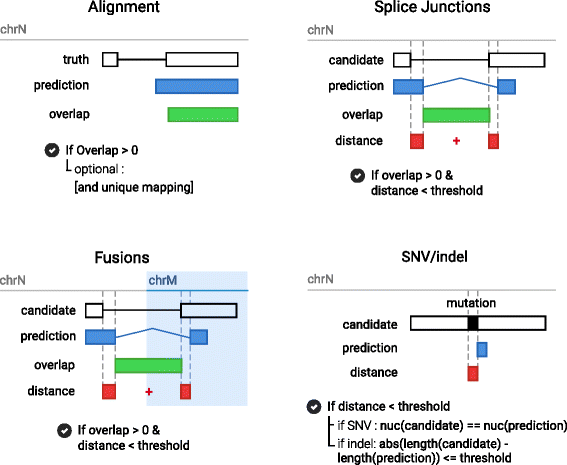
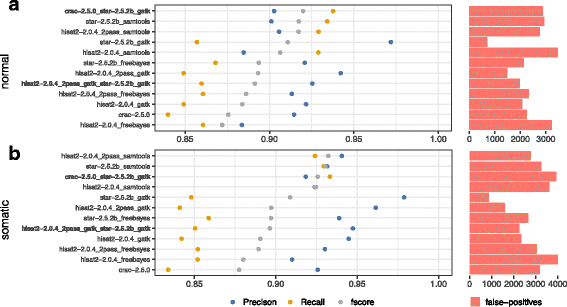
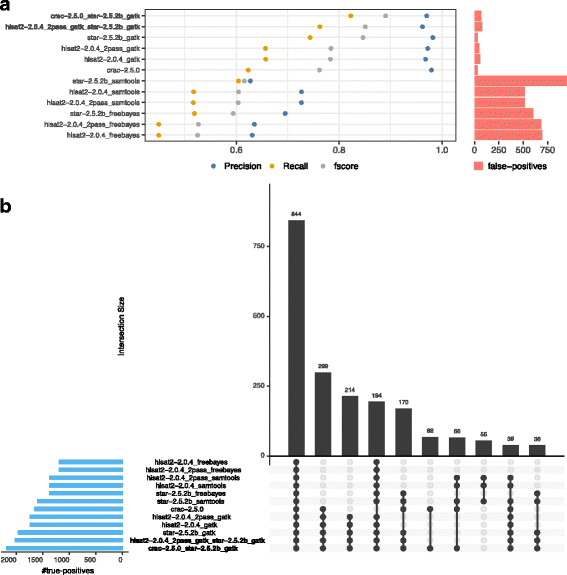
Results: To evaluate RNA-Seq pipelines, we developed a suite of two benchmarking tools. SimCT generates simulated datasets that get as close as possible to specific real biological conditions accompanied by the list of genomic incidents and mutations that have been inserted. BenchCT then compares the output of any bioinformatics pipeline that has been run against a SimCT dataset with the simulated genomic and transcriptional variations it contains to give an accurate performance evaluation in addressing specific biological question. We used these tools to simulate a real-world genomic medicine question s involving the comparison of healthy and cancerous cells. Results revealed that performance in addressing a particular biological context varied significantly depending on the choice of tools and settings used. We also found that by combining the output of certain pipelines, substantial performance improvements could be achieved.
Conclusion: Our research emphasizes the importance of selecting and configuring bioinformatic tools for the specific biological question being investigated to obtain optimal results. Pipeline designers, developers and users should include benchmarking in the context of their biological question as part of their design and quality control process. Our SimBA suite of benchmarking tools provides a reliable basis for comparing the performance of RNA-Seq bioinformatics pipelines in addressing a specific biological question. We would like to see the creation of a reference corpus of data-sets that would allow accurate comparison between benchmarks performed by different groups and the publication of more benchmarks based on this public corpus. SimBA software and data-set are available at http://cractools.gforge.inria.fr/softwares/simba/ .
Keywords: Benchmark; Pipeline optimization; RNA-Seq; Transcriptomics.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

Similar articles
-
SPARTA: Simple Program for Automated reference-based bacterial RNA-seq Transcriptome Analysis.BMC Bioinformatics. 2016 Feb 4;17:66. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-0923-y. BMC Bioinformatics. 2016. PMID: 26847232 Free PMC article.
-
Elucidating the editome: bioinformatics approaches for RNA editing detection.Brief Bioinform. 2019 Mar 22;20(2):436-447. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbx129. Brief Bioinform. 2019. PMID: 29040360 Review.
-
QuickRNASeq lifts large-scale RNA-seq data analyses to the next level of automation and interactive visualization.BMC Genomics. 2016 Jan 8;17:39. doi: 10.1186/s12864-015-2356-9. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 26747388 Free PMC article.
-
Indel sensitive and comprehensive variant/mutation detection from RNA sequencing data for precision medicine.BMC Med Genomics. 2018 Sep 14;11(Suppl 3):67. doi: 10.1186/s12920-018-0391-5. BMC Med Genomics. 2018. PMID: 30255803 Free PMC article.
-
Assembling and Validating Bioinformatic Pipelines for Next-Generation Sequencing Clinical Assays.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020 Sep 1;144(9):1118-1130. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0476-RA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32045276 Review.
Cited by
-
Challenges and best practices in omics benchmarking.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 May;25(5):326-339. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00679-6. Epub 2024 Jan 12. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 38216661 Review.
-
Fusion InPipe, an integrative pipeline for gene fusion detection from RNA-seq data in acute pediatric leukemia.Front Mol Biosci. 2023 Jun 9;10:1141310. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2023.1141310. eCollection 2023. Front Mol Biosci. 2023. PMID: 37363396 Free PMC article.
-
Mutation-Simulator: fine-grained simulation of random mutations in any genome.Bioinformatics. 2021 May 1;37(4):568-569. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btaa716. Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 32780803 Free PMC article.
-
BEERS2: RNA-Seq simulation through high fidelity in silico modeling.Brief Bioinform. 2024 Mar 27;25(3):bbae164. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbae164. Brief Bioinform. 2024. PMID: 38605641 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Seo JS, Ju YS, Lee WC, Shin JY, Lee JK, Bleazard T, Lee J, Jung YJ, Kim JO, Shin JY, Yu SB, Kim J, Lee ER, Kang CH, Park IK, Rhee H, Lee SH, Kim JI, Kang JH, Kim YT. The transcriptional landscape and mutational profile of lung adenocarcinoma. Genome Res. 2012. doi:10.1101/gr.145144.112. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

