How do we define the policy impact of public health research? A systematic review
- PMID: 28969650
- PMCID: PMC5625646
- DOI: 10.1186/s12961-017-0247-z
How do we define the policy impact of public health research? A systematic review
Abstract
Background: In order to understand and measure the policy impact of research we need a definition of research impact that is suited to the task. This article systematically reviewed both peer-reviewed and grey literature for definitions of research impact to develop a definition of research impact that can be used to investigate how public health research influences policy.
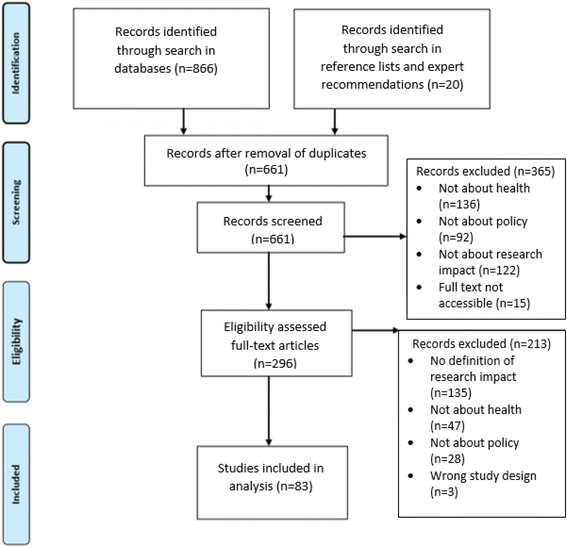
Method: Keyword searches of the electronic databases Web of Science, ProQuest, PubMed, EMBASE, CINAHL, Informit, PsycINFO, The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews and Google Scholar were conducted between August 2015 and April 2016. Keywords included 'definition' and 'policy' and 'research impact' or 'research evidence'. The search terms 'health', public health' or 'mental health' and 'knowledge transfer' or 'research translation' were used to focus the search on relevant health discipline approaches. Studies included in the review described processes, theories or frameworks associated with public health, health services or mental health policy.
Results: We identified 108 definitions in 83 publications. The key findings were that literature on research impact is growing, but only 23% of peer-reviewed publications on the topic explicitly defined the term and that the majority (76%) of definitions were derived from research organisations and funding institutions. We identified four main types of definition, namely (1) definitions that conceptualise research impacts in terms of positive changes or effects that evidence can bring about when transferred into policies (example Research Excellence Framework definition), (2) definitions that interpret research impacts as measurable outcomes (Research Councils UK), and (3) bibliometric and (4) use-based definitions. We identified four constructs underpinning these definitions that related to concepts of contribution, change, avenues and levels of impact.
Conclusion: The dominance of bureaucratic definitions, the tendency to discuss but not define the concept of research impact, and the heterogeneity of definitions confirm the need for conceptual clarity in this area. We propose a working definition of research impact that can be used in a range of health policy contexts.
Keywords: Definitions; Evidence-informed policies; Policy; Policy impact; Research; Research impact.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Eliciting adverse effects data from participants in clinical trials.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018 Jan 16;1(1):MR000039. doi: 10.1002/14651858.MR000039.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 29372930 Free PMC article.
-
Home treatment for mental health problems: a systematic review.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(15):1-139. doi: 10.3310/hta5150. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532236
-
The measurement and monitoring of surgical adverse events.Health Technol Assess. 2001;5(22):1-194. doi: 10.3310/hta5220. Health Technol Assess. 2001. PMID: 11532239
-
Factors that influence parents' and informal caregivers' views and practices regarding routine childhood vaccination: a qualitative evidence synthesis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021 Oct 27;10(10):CD013265. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013265.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2021. PMID: 34706066 Free PMC article.
-
Cost-effectiveness of using prognostic information to select women with breast cancer for adjuvant systemic therapy.Health Technol Assess. 2006 Sep;10(34):iii-iv, ix-xi, 1-204. doi: 10.3310/hta10340. Health Technol Assess. 2006. PMID: 16959170
Cited by
-
Looking both ways: a review of methods for assessing research impacts on policy and the policy utilisation of research.Health Res Policy Syst. 2018 Jun 25;16(1):54. doi: 10.1186/s12961-018-0310-4. Health Res Policy Syst. 2018. PMID: 29940961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
What should governments be doing to prevent diabetes throughout the life course?Diabetologia. 2019 Oct;62(10):1842-1853. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-4941-y. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Diabetologia. 2019. PMID: 31451873 Review.
-
Enhancing Impact: A Call to Action for Equitable Implementation Science.Prev Sci. 2024 Apr;25(Suppl 1):174-189. doi: 10.1007/s11121-023-01589-z. Epub 2023 Oct 25. Prev Sci. 2024. PMID: 37878237 Free PMC article.
-
[Public policy on palliative care and its implications for services, opioids, and education in ColombiaPolítica pública de cuidados paliativos e suas implicares para servidos, opioides e educaao na Colombia].Rev Cuid. 2023 Sep 2;14(2):e02. doi: 10.15649/cuidarte.2501. eCollection 2023 May-Aug. Rev Cuid. 2023. PMID: 40115200 Free PMC article. Spanish.
-
How do organisations implement research impact assessment (RIA) principles and good practice? A narrative review and exploratory study of four international research funding and administrative organisations.Health Res Policy Syst. 2020 Jan 20;18(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s12961-019-0515-1. Health Res Policy Syst. 2020. PMID: 31959198 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous