HDL cholesterol efflux normalised to apoA-I is associated with future development of type 2 diabetes: from the CORDIOPREV trial
- PMID: 28970513
- PMCID: PMC5624929
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12678-9
HDL cholesterol efflux normalised to apoA-I is associated with future development of type 2 diabetes: from the CORDIOPREV trial
Abstract
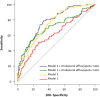
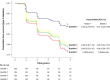
This prospective study evaluated whether baseline cholesterol efflux is associated with future development of type 2 diabetes (T2DM) in cardiovascular patients. We measured cholesterol efflux in all CORDIOPREV study (NCT00924937) participants free of T2DM at baseline (n = 462) and assessed its relationship with T2DM incidence during a 4.5 years of follow-up. Cholesterol efflux was quantified by incubation of cholesterol-loaded THP-1 cells with the participants' apoB-depleted plasma. Disposition index was estimated as beta-cell function indicator. During follow-up 106 individuals progressed to T2DM. The cholesterol efflux/apoA-1 ratio was inversely associated with T2DM development independently of traditional risk factors (model-1, OR: 0.647, 95%CI: 0.495-0.846), and after additional adjustment for glycaemic parameters (model-2, OR: 0.670, 95%CI: 0.511-0.878). When cumulative incidence of diabetes was analysed by quartiles of cholesterol efflux/apoA-I, incidence of T2DM was reduced by 54% in subjects who were in the higher cholesterol efflux/apoA-I quartile compared to subjects in the lowest quartile (p = 0.018 and p = 0.042 for model-1 and 2). Moreover, participants who were in the higher cholesterol efflux/apoA-I presented significantly higher disposition index (β = 0.056, SE = 0.026; p = 0.035). In conclusion, HDL-cholesterol efflux normalised to apoA-I was inversely associated with T2DM development in cardiovascular patients. This association was independent of several T2DM risk factors, and may be related to a preserved beta-cell function.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Association between cholesterol efflux capacity and peripheral artery disease in coronary heart disease patients with and without type 2 diabetes: from the CORDIOPREV study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Mar 25;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01260-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33766036 Free PMC article.
-
Different relationship between ANGPTL3 and HDL components in female non-diabetic subjects and type-2 diabetic patients.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016 Sep 13;15(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12933-016-0450-1. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2016. PMID: 27620179 Free PMC article.
-
HDL-C and HDL-C/ApoA-I predict long-term progression of glycemia in established type 2 diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2014 Aug;37(8):2351-8. doi: 10.2337/dc13-2738. Epub 2014 May 7. Diabetes Care. 2014. PMID: 24804699 Clinical Trial.
-
Plasma concentrations of lipoproteins and risk of lower-limb peripheral artery disease in people with type 2 diabetes: the SURDIAGENE study.Diabetologia. 2021 Mar;64(3):668-680. doi: 10.1007/s00125-020-05326-x. Epub 2021 Jan 6. Diabetologia. 2021. PMID: 33409569
-
[HDL-C/apoA-I]: A multivessel cardiometabolic risk marker in women with T2DM.Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018 Jan;34(1). doi: 10.1002/dmrr.2950. Epub 2017 Oct 16. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 28921828
Cited by
-
The relationship between polymorphism of insulin-like growth factor I gene and susceptibility to type 2 diabetes in Uygur population, Xinjiang, China.Genes Genomics. 2022 Apr;44(4):499-508. doi: 10.1007/s13258-021-01209-6. Epub 2022 Jan 30. Genes Genomics. 2022. PMID: 35094288 Free PMC article.
-
Association between cholesterol efflux capacity and peripheral artery disease in coronary heart disease patients with and without type 2 diabetes: from the CORDIOPREV study.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021 Mar 25;20(1):72. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01260-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2021. PMID: 33766036 Free PMC article.
-
Dysfunctional High-Density Lipoproteins in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Implications.J Clin Med. 2021 May 21;10(11):2233. doi: 10.3390/jcm10112233. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34063950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Insights of ANGPTL-3 on Modulating Cholesterol Efflux Capacity Induced by HDL Particle.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(6):771-779. doi: 10.2174/1566524023666230418104400. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37073658
-
APOLIPOPROTEIN E GENE POLYMORPHISMS AND PLASMA LIPIDS IN PERSONS LIVING WITH HIV: A CROSS SECTIONAL STUDY.Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024 Apr 30;22(1):8-13. Ann Ib Postgrad Med. 2024. PMID: 38939889 Free PMC article.
References
-
- World Health Organization: Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014. Geneva. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

