Influence of mismatched and bulged nucleotides on SNP-preferential RNase H cleavage of RNA-antisense gapmer heteroduplexes
- PMID: 28970564
- PMCID: PMC5624880
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12844-z
Influence of mismatched and bulged nucleotides on SNP-preferential RNase H cleavage of RNA-antisense gapmer heteroduplexes
Abstract
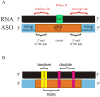
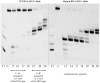
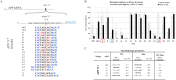
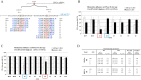
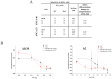
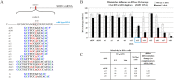
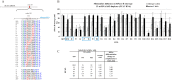
This study focused on determining design rules for gapmer-type antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs), that can differentiate cleavability of two SNP variants of RNA in the presence of ribonuclease H based on the mismatch type and position in the heteroduplex. We describe the influence of structural motifs formed by several arrangements of multiple mismatches (various types of mismatches and their position within the ASO/target RNA duplex) on RNase H cleavage selectivity of five different SNP types. The targets were mRNA fragments of APP, SCA3, SNCA and SOD1 genes, carrying C-to-G, G-to-C, G-to-A, A-to-G and C-to-U substitutions. The results show that certain arrangements of mismatches enhance discrimination between wild type and mutant SNP alleles of RNA in vitro as well as in HeLa cells. Among the over 120 gapmers tested, we found two gapmers that caused preferential degradation of the mutant allele APP 692 G and one that led to preferential cleavage of the mutant SNCA 53 A allele, both in vitro and in cells. However, several gapmers promoted selective cleavage of mRNA mutant alleles in in vitro experiments only.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Gapmer Antisense Oligonucleotides Containing 2',3'-Dideoxy-2'-fluoro-3'-C-hydroxymethyl-β-d-lyxofuranosyl Nucleotides Display Site-Specific RNase H Cleavage and Induce Gene Silencing.Chemistry. 2020 Jan 27;26(6):1368-1379. doi: 10.1002/chem.201904540. Epub 2020 Jan 20. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 31682037
-
A Tandem Oligonucleotide Approach for SNP-Selective RNA Degradation Using Modified Antisense Oligonucleotides.PLoS One. 2015 Nov 6;10(11):e0142139. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0142139. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26544037 Free PMC article.
-
Differential effects on allele selective silencing of mutant huntingtin by two stereoisomers of α,β-constrained nucleic acid.ACS Chem Biol. 2014 Sep 19;9(9):1975-9. doi: 10.1021/cb5003027. Epub 2014 Jul 25. ACS Chem Biol. 2014. PMID: 25050989
-
RNase cleavage-based methods for mutation/SNP detection, past and present.Hum Mutat. 2001 Sep;18(3):190-204. doi: 10.1002/humu.1175. Hum Mutat. 2001. PMID: 11524730 Review.
-
DNA-RNA Heteroduplex Oligonucleotide for Highly Efficient Gene Silencing.Methods Mol Biol. 2020;2176:113-119. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-0771-8_8. Methods Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 32865786 Review.
Cited by
-
Reduction of Off-Target Effects of Gapmer Antisense Oligonucleotides by Oligonucleotide Extension.Mol Diagn Ther. 2022 Jan;26(1):117-127. doi: 10.1007/s40291-021-00573-z. Epub 2022 Jan 7. Mol Diagn Ther. 2022. PMID: 34994962 Free PMC article.
-
Hybridization-mediated off-target effects of splice-switching antisense oligonucleotides.Nucleic Acids Res. 2020 Jan 24;48(2):802-816. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkz1132. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020. PMID: 31802121 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic study on the influence of thermodynamic asymmetry of 5'-ends of siRNA duplexes in relation to their silencing potency.Sci Rep. 2019 Feb 21;9(1):2477. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-36620-9. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30792489 Free PMC article.
-
Antisense Oligonucleotide-Based Downregulation of the G56R Pathogenic Variant Causing NR2E3-Associated Autosomal Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa.Genes (Basel). 2019 May 10;10(5):363. doi: 10.3390/genes10050363. Genes (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31083481 Free PMC article.
-
Strategies to improve the design of gapmer antisense oligonucleotide on allele-specific silencing.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jun 5;35(3):102237. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102237. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 38993932 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

