Selective Homogeneous Assay for Circulating Endopeptidase Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)
- PMID: 28970566
- PMCID: PMC5624913
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-12900-8
Selective Homogeneous Assay for Circulating Endopeptidase Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP)
Abstract
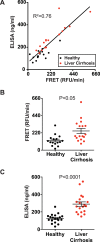
Fibroblast Activation Protein (FAP) is a membrane-bound serine protease whose expression is often elevated in activated fibroblasts associated with tissue remodeling in various common diseases such as cancer, arthritis and fibrosis. Like the closely related dipeptidyl peptidase DPPIV, the extracellular domain of FAP can be released into circulation as a functional enzyme, and limited studies suggest that the circulating level of FAP correlates with the degree of tissue fibrosis. Here we describe a novel homogeneous fluorescence intensity assay for circulating FAP activity based on a recently identified natural substrate, FGF21. This assay is unique in that it can effectively distinguish endopeptidase activity of FAP from that of other related enzymes such as prolyl endopeptidase (PREP) and was validated using Fap-deficient mice. Structural modeling was used to elucidate the mechanistic basis for the observed specificity in substrate recognition by FAP, but not by DPPIV or PREP. Finally, the assay was used to detect elevated FAP activity in human patients diagnosed with liver cirrhosis and to determine the effectiveness of a chemical inhibitor for FAP in mice. We propose that the assay presented here could thus be utilized for diagnosis of FAP-related pathologies and for the therapeutic development of FAP inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
This work was funded by Genentech, Inc. All the authors are present or former paid employees of Genentech/Roche. Genentech has filed patent applications related to this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Increased expression of fibroblast activation protein-alpha in keloid fibroblasts: implications for development of a novel treatment option.Arch Dermatol Res. 2010 Dec;302(10):725-31. doi: 10.1007/s00403-010-1084-x. Epub 2010 Sep 26. Arch Dermatol Res. 2010. PMID: 20872224
-
Fibroblast activation protein: a cell surface dipeptidyl peptidase and gelatinase expressed by stellate cells at the tissue remodelling interface in human cirrhosis.Hepatology. 1999 Jun;29(6):1768-78. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290631. Hepatology. 1999. PMID: 10347120
-
Fibroblast activation protein-α in fibrogenic disorders and cancer: more than a prolyl-specific peptidase?Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017 Oct;21(10):977-991. doi: 10.1080/14728222.2017.1370455. Epub 2017 Aug 30. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2017. PMID: 28829211 Review.
-
Identification of Novel Natural Substrates of Fibroblast Activation Protein-alpha by Differential Degradomics and Proteomics.Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019 Jan;18(1):65-85. doi: 10.1074/mcp.RA118.001046. Epub 2018 Sep 26. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2019. PMID: 30257879 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast activation protein in liver fibrosis.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019 Jan 1;24(1):1-17. doi: 10.2741/4706. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2019. PMID: 30468644 Review.
Cited by
-
Pro-tumorigenic roles of fibroblast activation protein in cancer: back to the basics.Oncogene. 2018 Aug;37(32):4343-4357. doi: 10.1038/s41388-018-0275-3. Epub 2018 May 3. Oncogene. 2018. PMID: 29720723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered expression of fibroblast activation protein-α (FAP) in colorectal adenoma-carcinoma sequence and in lymph node and liver metastases.Aging (Albany NY). 2020 May 19;12(11):10337-10358. doi: 10.18632/aging.103261. Epub 2020 May 19. Aging (Albany NY). 2020. PMID: 32428869 Free PMC article.
-
Role and mechanism of fibroblast-activated protein-α expression on the surface of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Front Immunol. 2023 Mar 17;14:1135384. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135384. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37006278 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Tissue and Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Activation Protein-α (FAP) in Renal Tumours.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Nov 16;12(11):3393. doi: 10.3390/cancers12113393. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33207686 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of Fibroblast Activation Protein by Transforming Growth Factor Beta-1 in Glioblastoma Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 21;22(3):1046. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031046. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33494271 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rettig WJ, et al. Regulation and heteromeric structure of the fibroblast activation protein in normal and transformed cells of mesenchymal and neuroectodermal origin. Cancer Res. 1993;53:3327–3335. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

