Iatrogenic Bilateral Simultaneous Pneumothorax: Call for Vigilance
- PMID: 28970663
- PMCID: PMC5613615
- DOI: 10.4103/ijccm.IJCCM_108_17
Iatrogenic Bilateral Simultaneous Pneumothorax: Call for Vigilance
Abstract
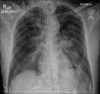
Iatrogenic pneumothorax refers to the pneumothorax generated after diagnostic or therapeutic procedure. We report the case of a 40-year-old male who had bilateral simultaneous iatrogenic pneumothorax with pneumomediastinum leading to cardiac arrest situation, due to wrong placement of nebulization kit in spontaneously breathing intubated patient. We report this case for its rarity, due to the critical importance of this cause as a etiology of bilateral simultaneous iatrogenic pneumothorax leading to cardiac arrest situation, and need to understand the importance of continuous training and stress of emergency environment.
Keywords: Iatrogenic bilateral pneumothorax; pneumomediastinum; simultaneous iatrogenic bilateral pneumothorax.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Yarmus L, Feller-Kopman D. Pneumothorax in the critically ill patient. Chest. 2012;141:1098–105. - PubMed
-
- John J, Seifi A. Incidence of iatrogenic pneumothorax in the United States in teaching vs. non-teaching hospitals from 2000 to 2012. J Crit Care. 2016;34:66–8. - PubMed
-
- de Lassence A, Timsit JF, Tafflet M, Azoulay E, Jamali S, Vincent F, et al. Pneumothorax in the Intensive Care Unit: Incidence, risk factors, and outcome. Anesthesiology. 2006;104:5–13. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous