HPV8-E6 Interferes with Syntenin-2 Expression through Deregulation of Differentiation, Methylation and Phosphatidylinositide-Kinase Dependent Mechanisms
- PMID: 28970821
- PMCID: PMC5609557
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.01724
HPV8-E6 Interferes with Syntenin-2 Expression through Deregulation of Differentiation, Methylation and Phosphatidylinositide-Kinase Dependent Mechanisms
Abstract
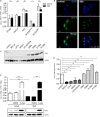
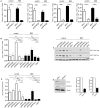
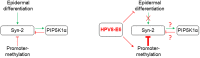
The E6 oncoproteins of high-risk human papillomaviruses (HPV) of genus alpha contain a short peptide sequence at the carboxy-terminus, the PDZ binding domain, with which they interact with the corresponding PDZ domain of cellular proteins. Interestingly, E6 proteins from papillomaviruses of genus beta (betaPV) do not encode a comparable PDZ binding domain. Irrespective of this fact, we previously showed that the E6 protein of HPV8 (betaPV type) could circumvent this deficit by targeting the PDZ protein Syntenin-2 through transcriptional repression (Lazic et al., 2012). Despite its high binding affinity to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PI(4,5)P2), very little is known about Syntenin-2. This study aimed to extend the knowledge on Syntenin-2 and how its expression is controlled. We now identified that Syntenin-2 is expressed at high levels in differentiating and in lower amounts in keratinocytes cultured in serum-free media containing low calcium concentration. HPV8-E6 led to a further reduction of Syntenin-2 expression only in cells cultured in low calcium. In the skin of patients suffering from Epidermodysplasia verruciformis, who are predisposed to betaPV infection, Syntenin-2 was expressed in differentiating keratinocytes of non-lesional skin, but was absent in virus positive squamous tumors. Using 5-Aza-2'-deoxycytidine, which causes DNA demethylation, Syntenin-2 transcription was profoundly activated and fully restored in the absence and presence of HPV8-E6, implicating that E6 mediated repression of Syntenin-2 transcription is due to promoter hypermethylation. Since Syntenin-2 binds to PI(4,5)P2, we further tested whether the PI(4,5)P2 metabolic pathway might govern Syntenin-2 expression. PI(4,5)P2 is generated by the activity of phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate-5-kinase type I (PIP5KI) or phosphatidylinositol-5-phosphate-4-kinase type II (PIP4KII) isoforms α, β and γ. Phosphatidylinositide kinases have recently been identified as regulators of gene transcription. Surprisingly, transfection of siRNAs directed against PIP5KI and PIP4KII resulted in higher Syntenin-2 expression with the highest effect mediated by siPIP5KIα. HPV8-E6 was able to counteract siPIP4KIIα, siPIP4KIIβ and siPIP5KIγ mediated Syntenin-2 re-expression but not siPIP5KIα. Finally, we identified Syntenin-2 as a key factor regulating PIP5KIα expression. Collectively, our data demonstrates that Syntenin-2 is regulated through multiple mechanisms and that downregulation of Syntenin-2 expression may contribute to E6 mediated dedifferentiation of infected skin cells.
Keywords: 5-bisphosphate; E6 oncoprotein; Syntenin-2; differentiation; human papillomavirus (HPV); methylation; phosphatidylinositol-4.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Human papillomavirus type 8 E6 oncoprotein inhibits transcription of the PDZ protein syntenin-2.J Virol. 2012 Aug;86(15):7943-52. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00132-12. Epub 2012 May 23. J Virol. 2012. PMID: 22623796 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The cutaneous beta human papillomavirus type 8 E6 protein induces CCL2 through the CEBPα/miR-203/p63 pathway to support an inflammatory microenvironment in epidermodysplasia verruciformis skin lesions.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Mar 6;14:1336492. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1336492. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38510961 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of C/EBPα as a novel target of the HPV8 E6 protein regulating miR-203 in human keratinocytes.PLoS Pathog. 2017 Jun 22;13(6):e1006406. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1006406. eCollection 2017 Jun. PLoS Pathog. 2017. PMID: 28640877 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of TGF-β and NOTCH Signaling by Cutaneous Papillomaviruses.Front Microbiol. 2018 Mar 8;9:389. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00389. eCollection 2018. Front Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29568286 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The biology of beta human papillomaviruses.Virus Res. 2017 Mar 2;231:128-138. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2016.11.013. Epub 2016 Nov 14. Virus Res. 2017. PMID: 27856220 Review.
Cited by
-
Phospholipidation of nuclear proteins by the human papillomavirus E6 oncoprotein: implication in carcinogenesis.Oncotarget. 2018 Sep 25;9(75):34142-34158. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.26140. eCollection 2018 Sep 25. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 30344928 Free PMC article.
-
Mucosal and Cutaneous Human Papillomavirus Infections and Cancer Biology.Front Oncol. 2019 May 8;9:355. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.00355. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31134154 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comparative Analysis of Alpha and Beta HPV E6 Oncoproteins: Insights into Functional Distinctions and Divergent Mechanisms of Pathogenesis.Viruses. 2023 Nov 14;15(11):2253. doi: 10.3390/v15112253. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 38005929 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Akgül B., Karle P., Adam M., Fuchs P. G., Pfister H. J. (2003). Dual role of tumor suppressor p53 in regulation of DNA replication and oncogene E6-promoter activity of epidermodysplasia verruciformis-associated human papillomavirus type 8. Virology 308 279–290. 10.1016/S0042-6822(02)00133-2 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

