Azidophenyl as a click-transformable redox label of DNA suitable for electrochemical detection of DNA-protein interactions
- PMID: 28970873
- PMCID: PMC5618110
- DOI: 10.1039/c4sc01906g
Azidophenyl as a click-transformable redox label of DNA suitable for electrochemical detection of DNA-protein interactions
Abstract
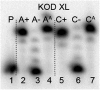
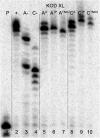
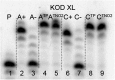
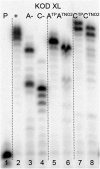
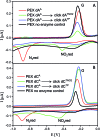
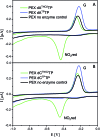
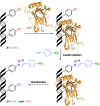
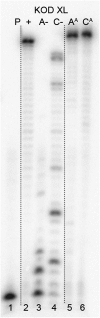
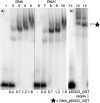
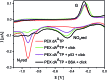
New redox labelling of DNA by an azido group which can be chemically transformed to nitrophenyltriazole or silenced to phenyltriazole was developed and applied to the electrochemical detection of DNA-protein interactions. 5-(4-Azidophenyl)-2'-deoxycytidine and 7-(4-azidophenyl)-7-deaza-2'-deoxyadenosine nucleosides were prepared by aqueous-phase Suzuki cross-coupling and converted to nucleoside triphosphates (dNTPs) which served as substrates for incorporation into DNA by DNA polymerase. The azidophenyl-modified nucleotides and azidophenyl-modified DNA gave a strong signal in voltammetric studies, at -0.9 V, due to reduction of the azido function. The Cu-catalyzed click reaction of azidophenyl-modified nucleosides or azidophenyl-modified DNA with 4-nitrophenylacetylene gave nitrophenyl-substituted triazoles, exerting a reduction peak at -0.4 V under voltammetry, whereas the click reaction with phenylacetylene gave electrochemically silent phenyltriazoles. The transformation of the azidophenyl label to nitrophenyltriazole was used for electrochemical detection of DNA-protein interactions (p53 protein) since only those azidophenyl groups in the parts of the DNA not shielded by the bound p53 protein were transformed to nitrophenyltriazoles, whereas those covered by the protein were not.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Phenothiazine-linked nucleosides and nucleotides for redox labelling of DNA.Org Biomol Chem. 2017 Aug 23;15(33):6984-6996. doi: 10.1039/c7ob01439b. Org Biomol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28792547
-
Aqueous Heck cross-coupling preparation of acrylate-modified nucleotides and nucleoside triphosphates for polymerase synthesis of acrylate-labeled DNA.J Org Chem. 2013 Oct 4;78(19):9627-37. doi: 10.1021/jo4011574. Epub 2013 Sep 16. J Org Chem. 2013. PMID: 23992435
-
Benzofurazane as a new redox label for electrochemical detection of DNA: towards multipotential redox coding of DNA bases.Chemistry. 2013 Sep 16;19(38):12720-31. doi: 10.1002/chem.201301868. Epub 2013 Aug 9. Chemistry. 2013. PMID: 23934942
-
Anthraquinone as a redox label for DNA: synthesis, enzymatic incorporation, and electrochemistry of anthraquinone-modified nucleosides, nucleotides, and DNA.Chemistry. 2011 Dec 9;17(50):14063-73. doi: 10.1002/chem.201101883. Epub 2011 Nov 17. Chemistry. 2011. PMID: 22095665
-
Cross-coupling reactions of nucleoside triphosphates followed by polymerase incorporation. Construction and applications of base-functionalized nucleic acids.Org Biomol Chem. 2008 Jul 7;6(13):2233-41. doi: 10.1039/b803664k. Epub 2008 Apr 2. Org Biomol Chem. 2008. PMID: 18563253 Review.
Cited by
-
Tuning of Oxidation Potential of Ferrocene for Ratiometric Redox Labeling and Coding of Nucleotides and DNA.Chemistry. 2020 Jan 27;26(6):1286-1291. doi: 10.1002/chem.201904700. Epub 2020 Jan 9. Chemistry. 2020. PMID: 31725178 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 by using a ratiometric colorimetric test based on click-mediated growth of gold nanoparticles.Mikrochim Acta. 2018 Sep 12;185(10):451. doi: 10.1007/s00604-018-2992-2. Mikrochim Acta. 2018. PMID: 30209641
-
Efficient enzymatic synthesis and dual-colour fluorescent labelling of DNA probes using long chain azido-dUTP and BCN dyes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2016 May 5;44(8):e79. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw028. Epub 2016 Jan 26. Nucleic Acids Res. 2016. PMID: 26819406 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced preparation of fragment libraries enabled by oligonucleotide-modified 2',3'-dideoxynucleotides.Commun Chem. 2022 Mar 16;5(1):34. doi: 10.1038/s42004-022-00649-9. Commun Chem. 2022. PMID: 36697673 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen-Centered Radicals Derived from Azidonucleosides.Molecules. 2024 May 14;29(10):2310. doi: 10.3390/molecules29102310. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38792171 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Paleček E., Jelen F. in Electrochemistry of nucleic acids and proteins: Towards electrochemical sensors for genomics and proteomics, ed. E. Paleček, F. Scheller, J. Wang, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005, pp. 74–174.
- Wang J., in Electrochemistry of nucleic acids and proteins: Towards electrochemical sensors for genomics and proteomics, ed. E. Paleček, F. Scheller, J. Wang, Elsevier, Amsterdam, 2005, pp. 175–194.
- Palecek E., Bartosik M. Chem. Rev. 2012;112:3427–3481. - PubMed
-
- Hocek M., Fojta M. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011;40:5802–5814. - PubMed
- Brázdilová P., Vrábel M., Pohl R., Pivoňková H., Havran L., Hocek M., Fojta M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2007;13:9527–9533. - PubMed
- Cahová H., Havran L., Brázdilová P., Pivoňková H., Pohl R., Fojta M., Hocek M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2008;47:2059–2062. - PubMed
- Balintová J., Pohl R., Horáková P., Vidláková P., Havran L., Fojta M., Hocek M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2011;17:14063–14073. - PubMed
- Macíčková-Cahová H., Pohl R., Horáková P., Havran L., Špaček J., Fojta M., Hocek M. Chem.–Eur. J. 2011;17:5833–5841. - PubMed
- Raindlová V., Pohl R., Klepetářová B., Havran L., Šimková E., Horáková P., Pivoňková H., Fojta M., Hocek M. ChemPlusChem. 2012;77:652–662.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

