Reduced acoustic noise in diffusion tensor imaging on a compact MRI system
- PMID: 28971512
- PMCID: PMC5843507
- DOI: 10.1002/mrm.26949
Reduced acoustic noise in diffusion tensor imaging on a compact MRI system
Abstract
Purpose: To investigate the feasibility of substantially reducing acoustic noise while performing diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) on a compact 3T (C3T) MRI scanner equipped with a 42-cm inner-diameter asymmetric gradient.
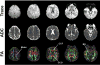
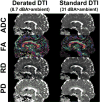
Methods: A-weighted acoustic measurements were made using 10 mT/m-amplitude sinusoidal waveforms, corresponding to echo-planar imaging (EPI) echo spacing of 0.25 to 5.0 ms, on a conventional, whole-body 3T MRI and on the C3T. Acoustic measurements of DTI with trapezoidal EPI waveforms were then made at peak gradient performance on the C3T (80 mT/m amplitude, 700 T/m/s slew rate) and at derated performance (33 mT/m, 10 to 50 T/m/s) for acoustic noise reduction. DTI was acquired in two different phantoms and in seven human subjects, with and without gradient-derating corresponding to multi- and single-shot acquisitions, respectively.
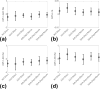
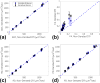
Results: Sinusoidal waveforms on the C3T were quieter by 8.5 to 15.6 A-weighted decibels (dBA) on average as compared to the whole-body MRI. The derated multishot DTI acquisition noise level was only 8.7 dBA (at 13 T/m/s slew rate) above ambient, and was quieter than non-derated, single-shot DTI by 22.3 dBA; however, the scan time was almost quadrupled. Although derating resulted in negligible diffusivity differences in the phantoms, small biases in diffusivity measurements were observed in human subjects (apparent diffusion coefficient = +9.3 ± 8.8%, fractional anisotropy = +3.2 ± 11.2%, radial diffusivity = +9.4 ± 16.8%, parallel diffusivity = +10.3 ± 8.4%).
Conclusion: The feasibility of achieving reduced acoustic noise levels with whole-brain DTI on the C3T MRI was demonstrated. Magn Reson Med 79:2902-2911, 2018. © 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Keywords: compact 3T; diffusion tensor imaging; head-only gradient; silent MRI.
© 2017 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Distortion-free imaging: A double encoding method (DIADEM) combined with multiband imaging for rapid distortion-free high-resolution diffusion imaging on a compact 3T with high-performance gradients.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Jan;51(1):296-310. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26792. Epub 2019 May 20. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31111581 Free PMC article.
-
Zoomed echo-planar diffusion tensor imaging for MR tractography of the prostate gland neurovascular bundle without an endorectal coil: a feasibility study.Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016 May;41(5):919-25. doi: 10.1007/s00261-015-0587-5. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2016. PMID: 27193790
-
Acoustic noise reduction for spiral MRI by gradient derating.Magn Reson Med. 2023 Oct;90(4):1547-1554. doi: 10.1002/mrm.29747. Epub 2023 Jun 22. Magn Reson Med. 2023. PMID: 37345705
-
Peripheral nerve diffusion tensor imaging: Overview, pitfalls, and future directions.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018 May;47(5):1171-1189. doi: 10.1002/jmri.25876. Epub 2017 Oct 30. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018. PMID: 29083521 Review.
-
Connectome 2.0: Developing the next-generation ultra-high gradient strength human MRI scanner for bridging studies of the micro-, meso- and macro-connectome.Neuroimage. 2021 Nov;243:118530. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118530. Epub 2021 Aug 28. Neuroimage. 2021. PMID: 34464739 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Distortion-free imaging: A double encoding method (DIADEM) combined with multiband imaging for rapid distortion-free high-resolution diffusion imaging on a compact 3T with high-performance gradients.J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020 Jan;51(1):296-310. doi: 10.1002/jmri.26792. Epub 2019 May 20. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2020. PMID: 31111581 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic Segmentation of Magnetic Resonance Images of Severe Patients with Advanced Liver Cancer and the Molecular Mechanism of Emodin-Induced Apoptosis of HepG2 Cells under the Deep Learning.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Mar 7;2022:3951112. doi: 10.1155/2022/3951112. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 35295165 Free PMC article.
-
The sensitivity of diffusion MRI to microstructural properties and experimental factors.J Neurosci Methods. 2021 Jan 1;347:108951. doi: 10.1016/j.jneumeth.2020.108951. Epub 2020 Oct 2. J Neurosci Methods. 2021. PMID: 33017644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hedeen RA, Edelstein WA. Characterization and prediction of gradient acoustic noise in MR imagers. Magn Reson Med. 1997;37(1):7–10. - PubMed
-
- Mansfield P, Glover PM, Beaumont J. Sound generation in gradient coil structures for MRI. Magn Reson Med. 1998;39(4):539–50. - PubMed
-
- Price DL, De Wilde JP, Papadaki AM, Curran JS, Kitney RI. Investigation of acoustic noise on 15 MRI scanners from 0.2 T to 3 T. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2001;13(2):288–93. - PubMed
-
- Chou I-J, Tench CR, Gowland P, Jaspan T, Dineen RA, Evangelou N, Abdel-Fahim R, Whitehouse WP, Constantinescu CS. Subjective discomfort in children receiving 3 T MRI and experienced adults’ perspective on children’s tolerability of 7 T: a cross-sectional questionnaire survey. BMJ open. 2014 doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2014-006094. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Moelker A, Maas RAJJ, Pattynama PMT. Verbal Communication in MR Environments: Effect of MR System Acoustic Noise on Speech Understanding. Radiology. 2004;232(1):107–13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

