Extracellular Cl- regulates electrical slow waves and setting of smooth muscle membrane potential by interstitial cells of Cajal in mouse jejunum
- PMID: 28971566
- PMCID: PMC5747553
- DOI: 10.1113/EP086367
Extracellular Cl- regulates electrical slow waves and setting of smooth muscle membrane potential by interstitial cells of Cajal in mouse jejunum
Abstract
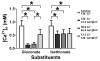
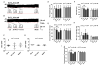
What is the central question of this study? The aim was to investigate the roles of extracellular chloride in electrical slow waves and resting membrane potential of mouse jejunal smooth muscle by replacing chloride with the impermeant anions gluconate and isethionate. What is the main finding and its importance? The main finding was that in smooth muscle cells, the resting Cl- conductance is low, whereas transmembrane Cl- movement in interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs) is a major contributor to the shape of electrical slow waves. Furthermore, the data confirm that ICCs set the smooth muscle membrane potential and that altering Cl- homeostasis in ICCs can alter the smooth muscle membrane potential. Intracellular Cl- homeostasis is regulated by anion-permeable channels and transporters and contributes to excitability of many cell types, including smooth muscle and interstitial cells of Cajal (ICCs). Our aims were to investigate the effects on electrical activity in mouse jejunal muscle strips of replacing extracellular Cl- (Cl-o ) with the impermeant anions gluconate and isethionate. On reducing Cl-o , effects were observed on electrical slow waves, with small effects on smooth muscle membrane voltage (Em ). Restoration of Cl- hyperpolarized smooth muscle Em proportional to the change in Cl-o concentration. Replacement of 90% of Cl-o with gluconate reversibly abolished slow waves in five of nine preparations. Slow waves were maintained in isethionate. Gluconate and isethionate substitution had similar concentration-dependent effects on peak amplitude, frequency, width at half peak amplitude, rise time and decay time of residual slow waves. Gluconate reduced free ionized Ca2+ in Krebs solutions to 0.13 mm. In Krebs solutions containing normal Cl- and 0.13 mm free Ca2+ , slow wave frequency was lower, width at half peak amplitude was smaller, and decay time was faster. The transient hyperpolarization following restoration of Cl-o was not observed in W/Wv mice, which lack pacemaker ICCs in the small intestine. We conclude that in smooth muscle cells, the resting Cl- conductance is low, whereas transmembrane Cl- movement in ICCs plays a major role in generation or propagation of slow waves. Furthermore, these data support a role for ICCs in setting smooth muscle Em and that altering Cl- homeostasis in ICCs can alter smooth muscle Em .
Keywords: chloride transport; gastrointestinal motility; pacemaker potentials.
© 2017 Mayo Clinic. Experimental Physiology © 2017 The Physiological Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Properties of pacemaker potentials recorded from myenteric interstitial cells of Cajal distributed in the mouse small intestine.J Physiol. 2003 Dec 15;553(Pt 3):803-18. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2003.051334. Epub 2003 Oct 17. J Physiol. 2003. PMID: 14565995 Free PMC article.
-
Role of calcium in activation of hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated channels caused by cholecystokinin octapeptide in interstitial cells of cajal.Digestion. 2012;85(4):266-75. doi: 10.1159/000337077. Epub 2012 Apr 24. Digestion. 2012. PMID: 22538231
-
Ionic basis of pacemaker generation in dog colonic smooth muscle.J Physiol. 1989 Sep;416:385-402. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1989.sp017767. J Physiol. 1989. PMID: 2481730 Free PMC article.
-
Spontaneous Electrical Activity and Rhythmicity in Gastrointestinal Smooth Muscles.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019;1124:3-46. doi: 10.1007/978-981-13-5895-1_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2019. PMID: 31183821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Generation and propagation of gastric slow waves.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010 Apr;37(4):516-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2009.05331.x. Epub 2009 Nov 23. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2010. PMID: 19930430 Review.
Cited by
-
Expression of the regulated isoform of the electrogenic Na+/HCO3- cotransporter, NBCe1, is enriched in pacemaker interstitial cells of Cajal.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021 Jan 1;320(1):G93-G107. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00255.2020. Epub 2020 Oct 28. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2021. PMID: 33112159 Free PMC article.
-
Bicarbonate ion transport by the electrogenic Na+ /HCO3- cotransporter, NBCe1, is required for normal electrical slow-wave activity in mouse small intestine.Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021 Sep;33(9):e14149. doi: 10.1111/nmo.14149. Epub 2021 Apr 10. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2021. PMID: 33837991 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Angeli TR, Cheng LK, Du P, Wang TH, Bernard CE, Vannucchi MG, Faussone-Pellegrini MS, Lahr C, Vather R, Windsor JA, Farrugia G, Abell TL, O’Grady G. Loss of Interstitial Cells of Cajal and Patterns of Gastric Dysrhythmia in Patients With Chronic Unexplained Nausea and Vomiting. Gastroenterology. 2015;149:56–66. e55. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

