Regulation and function of CMTR1-dependent mRNA cap methylation
- PMID: 28971629
- PMCID: PMC7169794
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1450
Regulation and function of CMTR1-dependent mRNA cap methylation
Abstract
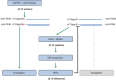
mRNA is modified co-transcriptionally at the 5' end by the addition of an inverted guanosine cap structure which can be methylated at several positions. The mRNA cap recruits proteins involved in gene expression and identifies the transcript as being cellular or 'self' in the innate immune response. Methylation of the first transcribed nucleotide on the ribose 2'-O position is a prevalent cap modification which has roles in splicing, translation and provides protection against the innate immune response. In this review, we discuss the regulation and function of CMTR1, the first transcribed nucleotide ribose 2'-O methyltransferase, and the molecular interactions which mediate methylated 2'-O ribose function. WIREs RNA 2017, 8:e1450. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1450 For further resources related to this article, please visit the WIREs website.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

