Human and nonhuman primate meninges harbor lymphatic vessels that can be visualized noninvasively by MRI
- PMID: 28971799
- PMCID: PMC5626482
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.29738
Human and nonhuman primate meninges harbor lymphatic vessels that can be visualized noninvasively by MRI
Abstract
Here, we report the existence of meningeal lymphatic vessels in human and nonhuman primates (common marmoset monkeys) and the feasibility of noninvasively imaging and mapping them in vivo with high-resolution, clinical MRI. On T2-FLAIR and T1-weighted black-blood imaging, lymphatic vessels enhance with gadobutrol, a gadolinium-based contrast agent with high propensity to extravasate across a permeable capillary endothelial barrier, but not with gadofosveset, a blood-pool contrast agent. The topography of these vessels, running alongside dural venous sinuses, recapitulates the meningeal lymphatic system of rodents. In primates, meningeal lymphatics display a typical panel of lymphatic endothelial markers by immunohistochemistry. This discovery holds promise for better understanding the normal physiology of lymphatic drainage from the central nervous system and potential aberrations in neurological diseases.
Keywords: MRI; human; human biology; lymphatics; marmoset monkey; medicine; meninges; neuroscience.
Conflict of interest statement
Dr. Absinta was partially supported by a National Multiple Sclerosis Society (NMSS) fellowship award #FG 2093-A-1 and holds a Marilyn Hilton Award for Innovation in MS research from the Conrad N. Hilton Foundation.
No competing interests declared.
Dr. Reich received research support from collaborations with the Myelin Repair Foundation and Vertex Pharmaceuticals, unrelated to the present study.
Figures
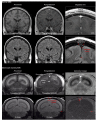
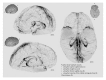
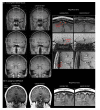
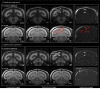
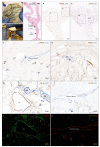
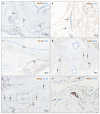

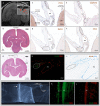
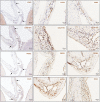
Comment in
-
Lymphatic Vessels Found in the Brain-Osteopathic Considerations, Part 2: Now in Humans and Monkeys.J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2018 Jan 1;118(1):53. doi: 10.7556/jaoa.2018.012. J Am Osteopath Assoc. 2018. PMID: 29309097 No abstract available.
References
-
- Absinta M, Nair G, Filippi M, Ray-Chaudhury A, Reyes-Mantilla MI, Pardo CA, Reich DS. Postmortem magnetic resonance imaging to guide the pathologic cut: individualized, 3-dimensionally printed cutting boxes for fixed brains. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology. 2014;73:780–788. doi: 10.1097/NEN.0000000000000096. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Absinta M, Vuolo L, Rao A, Nair G, Sati P, Cortese IC, Ohayon J, Fenton K, Reyes-Mantilla MI, Maric D, Calabresi PA, Butman JA, Pardo CA, Reich DS. Gadolinium-based MRI characterization of leptomeningeal inflammation in multiple sclerosis. Neurology. 2015;85:18–28. doi: 10.1212/WNL.0000000000001587. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Aspelund A, Tammela T, Antila S, Nurmi H, Leppänen VM, Zarkada G, Stanczuk L, Francois M, Mäkinen T, Saharinen P, Immonen I, Alitalo K. The Schlemm's canal is a VEGF-C/VEGFR-3-responsive lymphatic-like vessel. Journal of Clinical Investigation. 2014;124:3975–3986. doi: 10.1172/JCI75395. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

