Favorable impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia regardless of TP53 mutational status
- PMID: 28971906
- PMCID: PMC5709102
- DOI: 10.3324/haematol.2017.172544
Favorable impact of allogeneic stem cell transplantation in patients with therapy-related myelodysplasia regardless of TP53 mutational status
Abstract
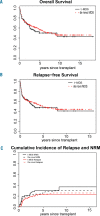
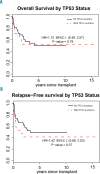
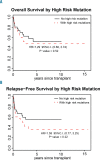
Therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome is a long-term complication of cancer treatment in patients receiving cytotoxic therapy, characterized by high-risk genetics and poor outcomes. Allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation is the only potential cure for this disease, but the prognostic impact of pre-transplant genetics and clinical features has not yet been fully characterized. We report here the genetic and clinical characteristics and outcomes of a relatively large cohort of patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome (n=67) who underwent allogeneic transplantation, comparing these patients to similarly treated patients with de novo disease (n=199). The 5-year overall survival was not different between patients with therapy-related and de novo disease (49.9% versus 53.9%; P=0.61) despite a higher proportion of individuals with an Intermediate-2/High International Prognostic Scoring System classification (59.7% versus 43.7%; P=0.003) and high-risk karyotypes (61.2% versus 30.7%; P<0.01) among the patients with therapy-related disease. In mutational analysis, TP53 alteration was the most common abnormality in patients with therapy-related disease (n=18: 30%). Interestingly, the presence of mutations in TP53 or in any other of the high-risk genes (EZH2, ETV6, RUNX1, ASXL1: n=29: 48%) did not significantly affect either overall survival or relapse-free survival. Allogeneic stem-cell transplantation is, therefore, a curative treatment for patients with therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome, conferring a similar long-term survival to that of patients with de novo disease despite higher-risk features. While TP53 alteration was the most common mutation in therapy-related myelodysplastic syndrome, the finding was not detrimental in our case-series.
Copyright© 2017 Ferrata Storti Foundation.
Figures

Comment in
-
Transplantation for therapy-related, TP53-mutated myelodysplastic syndrome - not because we can, but because we should.Haematologica. 2017 Dec;102(12):1970-1971. doi: 10.3324/haematol.2017.181180. Haematologica. 2017. PMID: 29192130 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Arber DA, Orazi A, Hasserjian R, et al. The 2016 revision to the World Health Organization classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia. Blood. 2016;127(20):2391–2405. - PubMed
-
- Vardiman JW, Thiele J, Arber DA, et al. The 2008 revision of the World Health Organization (WHO) classification of myeloid neoplasms and acute leukemia: rationale and important changes. Blood. 2009;114(5):937–951. - PubMed
-
- Kayser S, Dohner K, Krauter J, et al. The impact of therapy-related acute myeloid leukemia (AML) on outcome in 2853 adult patients with newly diagnosed AML. Blood. 2011;117(7):2137–2145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

