Secretory Autophagy in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Head and Neck Cancer Progression and Offers a Novel Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 28972076
- PMCID: PMC5712244
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-1077
Secretory Autophagy in Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts Promotes Head and Neck Cancer Progression and Offers a Novel Therapeutic Target
Abstract
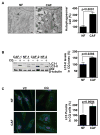
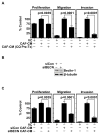
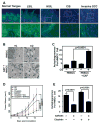
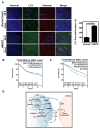
Despite therapeutic advancements, there has been little change in the survival of patients with head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC). Recent results suggest that cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) drive progression of this disease. Here, we report that autophagy is upregulated in HNSCC-associated CAFs, where it is responsible for key pathogenic contributions in this disease. Autophagy is fundamentally involved in cell degradation, but there is emerging evidence that suggests it is also important for cellular secretion. Thus, we hypothesized that autophagy-dependent secretion of tumor-promoting factors by HNSCC-associated CAFs may explain their role in malignant development. In support of this hypothesis, we observed a reduction in CAF-facilitated HNSCC progression after blocking CAF autophagy. Studies of cell growth media conditioned after autophagy blockade revealed levels of secreted IL6, IL8, and other cytokines were modulated by autophagy. Notably, when HNSCC cells were cocultured with normal fibroblasts, they upregulated autophagy through IL6, IL8, and basic fibroblast growth factor. In a mouse xenograft model of HNSCC, pharmacologic inhibition of Vps34, a key mediator of autophagy, enhanced the antitumor efficacy of cisplatin. Our results establish an oncogenic function for secretory autophagy in HNSCC stromal cells that promotes malignant progression. Cancer Res; 77(23); 6679-91. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 GM118247/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- S10 RR027564/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM103549/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA168524/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA024733/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR033179/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HD090216/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA020518/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA182872/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM122731/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000001/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103326/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P20 GM104936/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 AA020518/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

