CaMKII Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activity of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons and Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension
- PMID: 28972129
- PMCID: PMC5666588
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2141-17.2017
CaMKII Regulates Synaptic NMDA Receptor Activity of Hypothalamic Presympathetic Neurons and Sympathetic Outflow in Hypertension
Abstract
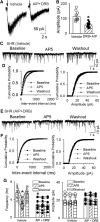
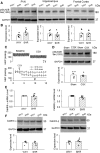
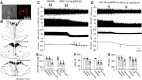
NMDAR activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) is increased and critically involved in heightened sympathetic vasomotor tone in hypertension. Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) binds to and modulates NMDAR activity. In this study, we determined the role of CaMKII in regulating NMDAR activity of PVN presympathetic neurons in male spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHRs). NMDAR-mediated EPSCs and puff NMDA-elicited currents were recorded in spinally projecting PVN neurons in SHRs and male Wistar-Kyoto (WKY) rats. The basal amplitude of evoked NMDAR-EPSCs and puff NMDA currents in retrogradely labeled PVN neurons were significantly higher in SHRs than in WKY rats. The CaMKII inhibitor autocamtide-2-related inhibitory peptide (AIP) normalized the increased amplitude of NMDAR-EPSCs and puff NMDA currents in labeled PVN neurons in SHRs but had no effect in WKY rats. Treatment with AIP also normalized the higher frequency of NMDAR-mediated miniature EPSCs of PVN neurons in SHRs. CaMKII-mediated phosphorylation level of GluN2B serine 1303 (S1303) in the PVN, but not in the hippocampus and frontal cortex, was significantly higher in SHRs than in WKY rats. Lowering blood pressure with celiac ganglionectomy in SHRs did not alter the increased level of phosphorylated GluN2B S1303 in the PVN. In addition, microinjection of AIP into the PVN significantly reduced arterial blood pressure and lumbar sympathetic nerve discharges in SHRs. Our findings suggest that CaMKII activity is increased in the PVN and contributes to potentiated presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDAR activity to elevate sympathetic vasomotor tone in hypertension.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT Heightened sympathetic vasomotor tone is a major contributor to the development of hypertension. Although glutamate NMDA receptor (NMDAR)-mediated excitatory drive in the hypothalamus plays a critical role in increased sympathetic output in hypertension, the molecular mechanism involved in potentiated NMDAR activity of hypothalamic presympathetic neurons remains unclear. Here we show that the activity of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) is increased and plays a key role in the potentiated presynaptic and postsynaptic NMDAR activity of hypothalamic presympathetic neurons in hypertension. Also, the inhibition of CaMKII in the hypothalamus reduces elevated blood pressure and sympathetic nerve discharges in hypertension. This new knowledge extends our understanding of the mechanism of synaptic plasticity in the hypothalamus and suggests new strategies to treat neurogenic hypertension.
Keywords: autonomic nervous system; hypertension; hypothalamus; sympathetic nerve activity; synaptic transmission.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/3710690-10$15.00/0.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
