Photorhabdus luminescens lectin A (PllA): A new probe for detecting α-galactoside-terminating glycoconjugates
- PMID: 28972138
- PMCID: PMC5712630
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.812792
Photorhabdus luminescens lectin A (PllA): A new probe for detecting α-galactoside-terminating glycoconjugates
Abstract
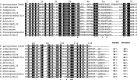
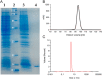
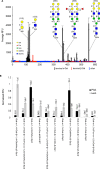
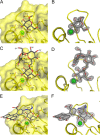
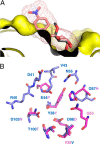
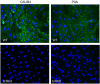
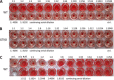
Lectins play important roles in infections by pathogenic bacteria, for example, in host colonization, persistence, and biofilm formation. The Gram-negative entomopathogenic bacterium Photorhabdus luminescens symbiotically lives in insect-infecting Heterorhabditis nematodes and kills the insect host upon invasion by the nematode. The P. luminescens genome harbors the gene plu2096, coding for a novel lectin that we named PllA. We analyzed the binding properties of purified PllA with a glycan array and a binding assay in solution. Both assays revealed a strict specificity of PllA for α-galactoside-terminating glycoconjugates. The crystal structures of apo PllA and complexes with three different ligands revealed the molecular basis for the strict specificity of this lectin. Furthermore, we found that a 90° twist in subunit orientation leads to a peculiar quaternary structure compared with that of its ortholog LecA from Pseudomonas aeruginosa We also investigated the utility of PllA as a probe for detecting α-galactosides. The α-Gal epitope is present on wild-type pig cells and is the main reason for hyperacute organ rejection in pig to primate xenotransplantation. We noted that PllA specifically recognizes this epitope on the glycan array and demonstrated that PllA can be used as a fluorescent probe to detect this epitope on primary porcine cells in vitro In summary, our biochemical and structural analyses of the P. luminescens lectin PllA have disclosed the structural basis for PllA's high specificity for α-galactoside-containing ligands, and we show that PllA can be used to visualize the α-Gal epitope on porcine tissues.
Keywords: carbohydrate; carbohydrate-binding protein; glycobiology; lectin; protein structure; structural biology.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures



References
-
- Poinar G. O., Thomas G. M., and Hess R. (1977) Characteristics of the specific bacterium associated with Heterorhabditis bacteriophora (Heterorhabditidae: Rhabditida). Nematologica 23, 97–102
-
- Thomas G. M., and Poinar J. R. (1979) Xenorhabdus gen. nov., a genus of entomopathogenic, nematophilic bacteria of the family Enterobacteriaceae. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 29, 352–360
-
- Boemare N., Akhurst R., and Mourant R. (1993) DNA relatedness between Xenorhabdus spp. (Enterobacteriaceae), symbiotic bacteria of entomopathogenic nematodes, and a proposal to transfer Xenorhabdus luminescens to a new genus, Photorhabdus gen. nov. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 43, 249–255
-
- Fischer-Le Saux M., Viallard V., Brunel B., Normand P., and Boemare N. E. (1999) Polyphasic classification of the genus Photorhabdus and proposal of new taxa: P. luminescens subsp. luminescens subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. akhurstii subsp. nov., P. luminescens subsp. laumondii subsp. nov., P. temperata sp. nov., P. temperata subsp. temperata subsp. nov., and P. asymbiotica sp. nov. Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 49, 1645–1656 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

