Surfactant protein A down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor by mechanisms different from those of surfactant protein D
- PMID: 28972165
- PMCID: PMC5682966
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.800771
Surfactant protein A down-regulates epidermal growth factor receptor by mechanisms different from those of surfactant protein D
Abstract
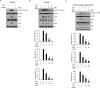
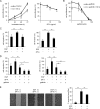
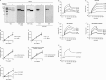
We recently reported that the lectin surfactant protein D (SP-D) suppresses epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling by interfering with ligand binding to EGFR through an interaction between the carbohydrate-recognition domain (CRD) of SP-D and N-glycans of EGFR. Here, we report that surfactant protein A (SP-A) also suppresses EGF signaling in A549 human lung adenocarcinoma cells and in CHOK1 cells stably expressing human EGFR and that SP-A inhibits the proliferation and motility of the A549 cells. Results with 125I-EGF indicated that SP-A interferes with EGF binding to EGFR, and a ligand blot analysis suggested that SP-A binds EGFR in A549 cells. We also found that SP-A directly binds the recombinant extracellular domain of EGFR (soluble EGFR or sEGFR), and this binding, unlike that of SP-D, was not blocked by EDTA, excess mannose, or peptide:N-glycosidase F treatment. We prepared a collagenase-resistant fragment (CRF) of SP-A, consisting of CRD plus the neck domain of SP-A, and observed that CRF directly binds sEGFR but does not suppress EGF-induced phosphorylation of EGFR in or proliferation of A549 cells. These results indicated that SP-A binds EGFR and down-regulates EGF signaling by inhibiting ligand binding to EGFR as well as SP-D. However, unlike for SP-D, SP-A lectin activity and EGFR N-glycans were not involved in the interaction between SP-A and EGFR. Furthermore, our results suggested that oligomerization of SP-A is necessary to suppress the effects of SP-A on EGF signaling.
Keywords: collectin; epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR); lung cancer; oligomerization; pulmonary surfactant.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures




Similar articles
-
Surfactant protein D suppresses lung cancer progression by downregulation of epidermal growth factor signaling.Oncogene. 2015 Feb 12;34(7):838-45. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.20. Epub 2014 Mar 10. Oncogene. 2015. PMID: 24608429
-
Epidermal growth factor receptors containing a single tyrosine in their C-terminal tail bind different effector molecules and are signaling-competent.J Biol Chem. 2017 Dec 15;292(50):20744-20755. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.802553. Epub 2017 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 29074618 Free PMC article.
-
Differential Ligand Binding Specificities of the Pulmonary Collectins Are Determined by the Conformational Freedom of a Surface Loop.Biochemistry. 2017 Aug 8;56(31):4095-4105. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b01313. Epub 2017 Jul 31. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28719181
-
Surfactant protein A and surfactant protein D variation in pulmonary disease.Immunobiology. 2007;212(4-5):381-416. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2007.01.003. Epub 2007 Feb 23. Immunobiology. 2007. PMID: 17544823 Review.
-
Ligands and receptors of lung surfactant proteins SP-A and SP-D.Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013 Jun 1;18(3):1129-40. doi: 10.2741/4168. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2013. PMID: 23747872 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Surfactant Protein D in Experimental Otitis Media.J Innate Immun. 2021;13(4):197-210. doi: 10.1159/000513605. Epub 2021 Feb 8. J Innate Immun. 2021. PMID: 33556949 Free PMC article.
-
Genetic disorders of the surfactant system: focus on adult disease.Eur Respir Rev. 2021 Feb 16;30(159):200085. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0085-2020. Print 2021 Mar 31. Eur Respir Rev. 2021. PMID: 33597124 Free PMC article.
-
Establishment and validation of nomogram for predicting immuno checkpoint inhibitor related pneumonia.BMC Pulm Med. 2022 Sep 1;22(1):331. doi: 10.1186/s12890-022-02127-3. BMC Pulm Med. 2022. PMID: 36050683 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Pulmonary Collectins, Surfactant Protein A (SP-A) and Surfactant Protein D (SP-D) in Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Sep 10;16(18):3116. doi: 10.3390/cancers16183116. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39335088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of four genes in exosomes as biomarkers for the identification of lung adenocarcinoma and lung squamous cell carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2021 Apr;21(4):249. doi: 10.3892/ol.2021.12510. Epub 2021 Feb 3. Oncol Lett. 2021. PMID: 33664813 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuroki Y., and Voelker D. R. (1994) Pulmonary surfactant proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 269, 25943–25946 - PubMed
-
- Whitsett J. A., and Weaver T. E. (2002) Hydrophobic surfactant proteins in lung function and disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 347, 2141–2148 - PubMed
-
- Kuroki Y., Takahashi M., and Nishitani C. (2007) Pulmonary collectins in innate immunity of the lung. Cell. Microbiol. 9, 1871–1879 - PubMed
-
- Wright J. R. (2005) Immunoregulatory functions of surfactant proteins. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 5, 58–68 - PubMed
-
- Crouch E., Hartshorn K., and Ofek I. (2000) Collectins and pulmonary innate immunity. Immunol. Rev. 173, 52–65 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

