NK3 homeobox 1 (NKX3.1) up-regulates forkhead box O1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and thereby suppresses tumor proliferation and invasion
- PMID: 28972178
- PMCID: PMC5702659
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.793760
NK3 homeobox 1 (NKX3.1) up-regulates forkhead box O1 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma and thereby suppresses tumor proliferation and invasion
Abstract
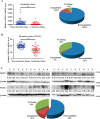
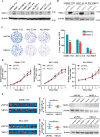
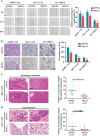
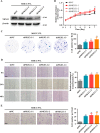
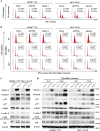
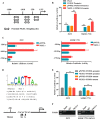
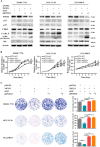
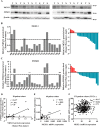
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the leading cause of cancer-related mortality in China, and the molecular mechanism of uncontrolled HCC progression remains to be explored. NK3 homeobox 1 (NKX3.1), an androgen-regulated prostate-specific transcription factor, suppresses tumors in prostate cancer, but its role in HCC is unknown, especially in hepatocellular carcinoma. In the present study, the differential expression analyses in HCC tissues and matched adjacent noncancerous liver tissues revealed that NKX3.1 is frequently down-regulated in human primary HCC tissues compared with matched adjacent noncancerous liver tissues. We also noted that NKX3.1 significantly inhibits proliferation and mobility of HCC cells both in vitro and in vivo Furthermore, NKX3.1 overexpression resulted in cell cycle arrest at the G1/S phase via direct binding to the promoter of forkhead box O1 (FOXO1) and up-regulation of expression. Of note, FOXO1 silencing in NKX3.1-overexpressing cells reversed the inhibitory effects of NKX3.1 on HCC cell proliferation and invasion. Consistently, both FOXO1 and NKX3.1 were down-regulated in human HCC tissues, and their expression was significantly and positively correlated with each other. These results suggest that NKX3.1 functions as a tumor suppressor in HCC cells through directly up-regulating FOXO1 expression.
Keywords: FOXO; NK3 Homeobox 1; cell proliferation; hepatocellular carcinoma; metastasis; tumor suppressor gene.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R. L., Miller K. D., and Jemal A. (2017) Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J. Clin. 67, 7–30 - PubMed
-
- Critelli R. M., De Maria N., and Villa E. (2015) Biology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Dig. Dis. 33, 635–641 - PubMed
-
- Ferlay J., Soerjomataram I., Dikshit R., Eser S., Mathers C., Rebelo M., Parkin D. M., Forman D., and Bray F. (2015) Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int. J. Cancer 136, E359–E386 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

