The hnRNP RALY regulates transcription and cell proliferation by modulating the expression of specific factors including the proliferation marker E2F1
- PMID: 28972179
- PMCID: PMC5712610
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.795591
The hnRNP RALY regulates transcription and cell proliferation by modulating the expression of specific factors including the proliferation marker E2F1
Abstract
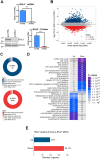
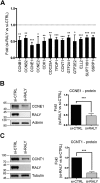
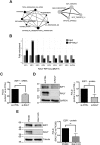
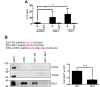
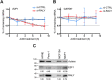
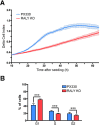
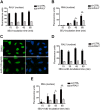
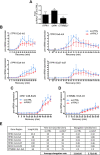
The heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNP) form a large family of RNA-binding proteins that exert numerous functions in RNA metabolism. RALY is a member of the hnRNP family that binds poly-U-rich elements within several RNAs and regulates the expression of specific transcripts. RALY is up-regulated in different types of cancer, and its down-regulation impairs cell cycle progression. However, the RALY's role in regulating RNA levels remains elusive. Here, we show that numerous genes coding for factors involved in transcription and cell cycle regulation exhibit an altered expression in RALY-down-regulated HeLa cells, consequently causing impairments in transcription, cell proliferation, and cell cycle progression. Interestingly, by comparing the list of RALY targets with the list of genes affected by RALY down-regulation, we found an enrichment of RALY mRNA targets in the down-regulated genes upon RALY silencing. The affected genes include the E2F transcription factor family. Given its role as proliferation-promoting transcription factor, we focused on E2F1. We demonstrate that E2F1 mRNA stability and E2F1 protein levels are reduced in cells lacking RALY expression. Finally, we also show that RALY interacts with transcriptionally active chromatin in both an RNA-dependent and -independent manner and that this association is abolished in the absence of active transcription. Taken together, our results highlight the importance of RALY as an indirect regulator of transcription and cell cycle progression through the regulation of specific mRNA targets, thus strengthening the possibility of a direct gene expression regulation exerted by RALY.
Keywords: E2F transcription factor; RNA; RNA metabolism; chromatin; heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein (hnRNP); hnRNP-associated with lethal yellow homolog (RALY).
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures
Similar articles
-
The hnRNP RALY regulates PRMT1 expression and interacts with the ALS-linked protein FUS: implication for reciprocal cellular localization.Mol Biol Cell. 2018 Dec 15;29(26):3067-3081. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-02-0108. Epub 2018 Oct 24. Mol Biol Cell. 2018. PMID: 30354839 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and dynamic changes of RNAs isolated from RALY-containing ribonucleoprotein complexes.Nucleic Acids Res. 2017 Jun 20;45(11):6775-6792. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx235. Nucleic Acids Res. 2017. PMID: 28379492 Free PMC article.
-
Proteome-wide characterization of the RNA-binding protein RALY-interactome using the in vivo-biotinylation-pulldown-quant (iBioPQ) approach.J Proteome Res. 2013 Jun 7;12(6):2869-84. doi: 10.1021/pr400193j. Epub 2013 May 6. J Proteome Res. 2013. PMID: 23614458
-
RALY may cause an aggressive biological behavior and a dismal prognosis in non-small-cell lung cancer.Exp Cell Res. 2020 Apr 15;389(2):111884. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.111884. Epub 2020 Feb 1. Exp Cell Res. 2020. PMID: 32014444
-
Biological functions and clinic significance of SAF‑A (Review).Biomed Rep. 2024 Apr 10;20(6):88. doi: 10.3892/br.2024.1776. eCollection 2024 Jun. Biomed Rep. 2024. PMID: 38665420 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nasal Septum Deviation as the Consequence of BMP-Controlled Changes to Cartilage Properties.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Jun 24;9:696545. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.696545. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34249945 Free PMC article.
-
DHX30 Coordinates Cytoplasmic Translation and Mitochondrial Function Contributing to Cancer Cell Survival.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Aug 31;13(17):4412. doi: 10.3390/cancers13174412. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34503222 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear ribonucleoprotein RALY downregulates foot-and-mouth disease virus replication but antagonized by viral 3C protease.Microbiol Spectr. 2024 Mar 5;12(3):e0365823. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03658-23. Epub 2024 Feb 7. Microbiol Spectr. 2024. PMID: 38323828 Free PMC article.
-
RALYL increases hepatocellular carcinoma stemness by sustaining the mRNA stability of TGF-β2.Nat Commun. 2021 Mar 9;12(1):1518. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-21828-7. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 33750796 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of RALY promotes migration and predicts poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Nov 9;10:5559-5572. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S182996. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30519104 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Sainsbury S., Bernecky C., and Cramer P. (2015) Structural basis of transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 16, 129–143 - PubMed
-
- Thomas M. C., and Chiang C. M. (2006) The general transcription machinery and general cofactors. Crit. Rev. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 41, 105–178 - PubMed
-
- Das R., Yu J., Zhang Z., Gygi M. P., Krainer A. R., Gygi S. P., and Reed R. (2007) SR proteins function in coupling RNAP II transcription to pre-mRNA splicing. Mol. Cell 26, 867–881 - PubMed
-
- Fackelmayer F. O., Dahm K., Renz A., Ramsperger U., and Richter A. (1994) Nucleic-acid-binding properties of hnRNP/SAF-A, a nuclear-matrix protein which binds DNA and RNA in vivo and in vitro. Eur. J. Biochem. 221, 749–757 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

