The actin-related p41ARC subunit contributes to p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1)-mediated glucose uptake into skeletal muscle cells
- PMID: 28972183
- PMCID: PMC5704484
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.801340
The actin-related p41ARC subunit contributes to p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1)-mediated glucose uptake into skeletal muscle cells
Abstract
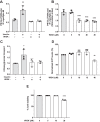
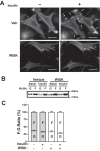
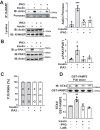
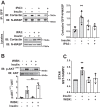
Defects in translocation of the glucose transporter GLUT4 are associated with peripheral insulin resistance, preclinical diabetes, and progression to type 2 diabetes. GLUT4 recruitment to the plasma membrane of skeletal muscle cells requires F-actin remodeling. Insulin signaling in muscle requires p21-activated kinase-1 (PAK1), whose downstream signaling triggers actin remodeling, which promotes GLUT4 vesicle translocation and glucose uptake into skeletal muscle cells. Actin remodeling is a cyclic process, and although PAK1 is known to initiate changes to the cortical actin-binding protein cofilin to stimulate the depolymerizing arm of the cycle, how PAK1 might trigger the polymerizing arm of the cycle remains unresolved. Toward this, we investigated whether PAK1 contributes to the mechanisms involving the actin-binding and -polymerizing proteins neural Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP), cortactin, and ARP2/3 subunits. We found that the actin-polymerizing ARP2/3 subunit p41ARC is a PAK1 substrate in skeletal muscle cells. Moreover, co-immunoprecipitation experiments revealed that insulin stimulates p41ARC phosphorylation and increases its association with N-WASP coordinately with the associations of N-WASP with cortactin and actin. Importantly, all of these associations were ablated by the PAK inhibitor IPA3, suggesting that PAK1 activation lies upstream of these actin-polymerizing complexes. Using the N-WASP inhibitor wiskostatin, we further demonstrated that N-WASP is required for localized F-actin polymerization, GLUT4 vesicle translocation, and glucose uptake. These results expand the model of insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells by implicating p41ARC as a new component of the insulin-signaling cascade and connecting PAK1 signaling to N-WASP-cortactin-mediated actin polymerization and GLUT4 vesicle translocation.
Keywords: actin; glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4); insulin resistance; insulin signaling; serine/threonine protein kinase PAK 1 (PAK1); skeletal muscle.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health
Figures

Similar articles
-
Signaling of the p21-activated kinase (PAK1) coordinates insulin-stimulated actin remodeling and glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cells.Biochem Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 15;92(2):380-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2014.08.033. Epub 2014 Sep 6. Biochem Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25199455 Free PMC article.
-
A phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-independent insulin signaling pathway to N-WASP/Arp2/3/F-actin required for GLUT4 glucose transporter recycling.J Biol Chem. 2002 Jan 4;277(1):509-15. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M108280200. Epub 2001 Nov 1. J Biol Chem. 2002. PMID: 11694514
-
Disruption of cortical actin in skeletal muscle demonstrates an essential role of the cytoskeleton in glucose transporter 4 translocation in insulin-sensitive tissues.J Biol Chem. 2004 Sep 24;279(39):40699-706. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M402697200. Epub 2004 Jul 6. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15247264 Free PMC article.
-
p21-Activated protein kinases and their emerging roles in glucose homeostasis.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Apr 1;306(7):E707-22. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00506.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24368667 Review.
-
Intracellular organization of insulin signaling and GLUT4 translocation.Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001;56:175-93. doi: 10.1210/rp.56.1.175. Recent Prog Horm Res. 2001. PMID: 11237212 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Different Exercise Training Protocols on Gene Expression of Rac1 and PAK1 in Healthy Rat Fast- and Slow-Type Muscles.Front Physiol. 2020 Nov 19;11:584661. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2020.584661. eCollection 2020. Front Physiol. 2020. PMID: 33329033 Free PMC article.
-
GLUT4 Trafficking and Storage Vesicles: Molecular Architecture, Regulatory Networks, and Their Disruption in Insulin Resistance.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Aug 5;26(15):7568. doi: 10.3390/ijms26157568. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40806697 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-catenin regulates muscle glucose transport via actin remodelling and M-cadherin binding.Mol Metab. 2020 Dec;42:101091. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2020.101091. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Mol Metab. 2020. PMID: 33011305 Free PMC article.
-
Rac1-PAK1 regulation of Rab11 cycling promotes junction destabilization.J Cell Biol. 2021 Jun 7;220(6):e202002114. doi: 10.1083/jcb.202002114. J Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33914026 Free PMC article.
-
Promoting Glucose Transporter-4 Vesicle Trafficking along Cytoskeletal Tracks: PAK-Ing Them Out.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017 Nov 20;8:329. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2017.00329. eCollection 2017. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017. PMID: 29209279 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Leto D., and Saltiel A. R. (2012) Regulation of glucose transport by insulin: traffic control of GLUT4. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 13, 383–396 - PubMed
-
- Foley K., Boguslavsky S., and Klip A. (2011) Endocytosis, recycling, and regulated exocytosis of glucose transporter 4. Biochemistry 50, 3048–3061 - PubMed
-
- Thiebaud D., Jacot E., DeFronzo R. A., Maeder E., Jequier E., and Felber J. P. (1982) The effect of graded doses of insulin on total glucose uptake, glucose oxidation, and glucose storage in man. Diabetes 31, 957–963 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

