Intramolecular autoinhibition of checkpoint kinase 1 is mediated by conserved basic motifs of the C-terminal kinase-associated 1 domain
- PMID: 28972186
- PMCID: PMC5704483
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M117.811265
Intramolecular autoinhibition of checkpoint kinase 1 is mediated by conserved basic motifs of the C-terminal kinase-associated 1 domain
Abstract
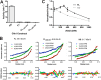
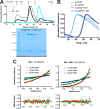
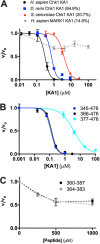
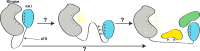
Precise control of the cell cycle allows for timely repair of genetic material prior to replication. One factor intimately involved in this process is checkpoint kinase 1 (Chk1), a DNA damage repair inducing Ser/Thr protein kinase that contains an N-terminal kinase domain and a C-terminal regulatory region consisting of a ∼100-residue linker followed by a putative kinase-associated 1 (KA1) domain. We report the crystal structure of the human Chk1 KA1 domain, demonstrating striking structural homology with other sequentially diverse KA1 domains. Separately purified Chk1 kinase and KA1 domains are intimately associated in solution, which results in inhibition of Chk1 kinase activity. Using truncation mutants and site-directed mutagenesis, we define the inhibitory face of the KA1 domain as a series of basic residues residing on two conserved regions of the primary structure. These findings point to KA1-mediated intramolecular autoinhibition as a key regulatory mechanism of human Chk1, and provide new therapeutic possibilities with which to attack this validated oncology target with small molecules.
Keywords: DNA damage response; cell cycle; checkpoint control; crystal structure; enzyme inactivation; enzyme mechanism; protein domain; serine/threonine protein kinase; structural biology.
© 2017 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest with the contents of this article
Figures


References
-
- Walworth N., Davey S., and Beach D. (1993) Fission yeast Chk1 protein kinase links the rad checkpoint pathway to cdc2. Nature 363, 368–371 - PubMed
-
- Sanchez Y., Wong C., Thoma R. S., Richman R., Wu Z., Piwnica-Worms H., and Elledge S. J. (1997) Conservation of the Chk1 checkpoint pathway in mammals: linkage of DNA damage to Cdk regulation through Cdc25. Science 277, 1497–1501 - PubMed
-
- Smits V. A., and Gillespie D. A. (2015) DNA damage control: regulation and functions of checkpoint kinase 1. FEBS J. 282, 3681–3692 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

