Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Ubiquitin in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinsonian Disorders
- PMID: 28972305
- PMCID: PMC5765402
- DOI: 10.1002/prca.201700100
Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Cerebrospinal Fluid Ubiquitin in Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinsonian Disorders
Abstract
Purpose: Dysfunctional proteostasis, with decreased protein degradation and an accumulation of ubiquitin into aggregated protein inclusions, is a feature of neurodegenerative diseases. Identifying new potential biomarkers in cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) reflecting this process could contribute important information on pathophysiology.
Experimental design: A developed method combining SPE and PRM-MS is employed to monitor the concentration of ubiquitin in CSF from subjects with Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), and progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP). Four independent cross-sectional studies are conducted, studies 1-4, including controls (n = 86) and participants with AD (n = 60), PD (n = 15), and PSP (n = 11).
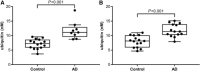
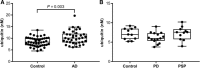
Results: The method shows a repeatability and intermediate precision not exceeding 6.1 and 7.9%, respectively. The determined LOD is 0.1 nm and the LOQ range between 0.625 and 80 nm. The CSF ubiquitin concentration is 1.2-1.5-fold higher in AD patients compared with controls in the three independent AD-control studies (Study 1, p < 0.001; Study 2, p < 0.001; and Study 3, p = 0.003). In the fourth study, there is no difference in PD or PSP, compared to controls.
Conclusion and clinical relevance: CSF ubiquitin may reflect dysfunctional proteostasis in AD. The described method can be used for further exploration of ubiquitin as a potential biomarker in neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: alzheimer's disease; biomarker; parkinson's disease; progressive supranuclear palsy; ubiquitin.
© 2017 The Authors. Published by WILEY-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Endo-lysosomal proteins and ubiquitin CSF concentrations in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Sep 14;11(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0533-9. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31521194 Free PMC article.
-
Intact protein analysis of ubiquitin in cerebrospinal fluid by multiple reaction monitoring reveals differences in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration.J Proteome Res. 2014 Nov 7;13(11):4518-25. doi: 10.1021/pr5006058. Epub 2014 Aug 13. J Proteome Res. 2014. PMID: 25091646
-
SCRN1: A cerebrospinal fluid biomarker correlating with tau in Alzheimer's disease.Alzheimers Dement. 2023 Oct;19(10):4609-4618. doi: 10.1002/alz.13042. Epub 2023 Mar 22. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. PMID: 36946611
-
Alzheimer's Disease-Related Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers in Progressive Supranuclear Palsy.Brain Sci. 2024 Aug 26;14(9):859. doi: 10.3390/brainsci14090859. Brain Sci. 2024. PMID: 39335355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mass spectrometry-based methods for robust measurement of Alzheimer's disease biomarkers in biological fluids.J Neurochem. 2021 Oct;159(2):211-233. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15465. Epub 2021 Aug 25. J Neurochem. 2021. PMID: 34244999 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Proteomic Approaches for the Discovery of Biofluid Biomarkers of Neurodegenerative Dementias.Proteomes. 2018 Aug 31;6(3):32. doi: 10.3390/proteomes6030032. Proteomes. 2018. PMID: 30200280 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proteomics Landscape of Alzheimer's Disease.Proteomes. 2021 Mar 10;9(1):13. doi: 10.3390/proteomes9010013. Proteomes. 2021. PMID: 33801961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CSF Ubiquitin Levels Are Higher in Alzheimer's Disease than in Frontotemporal Dementia and Reflect the Molecular Subtype in Prion Disease.Biomolecules. 2020 Mar 25;10(4):497. doi: 10.3390/biom10040497. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32218217 Free PMC article.
-
The Diagnostic Potential of Amyloidogenic Proteins.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 16;22(8):4128. doi: 10.3390/ijms22084128. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33923609 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endo-lysosomal proteins and ubiquitin CSF concentrations in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Sep 14;11(1):82. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0533-9. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 31521194 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bancher C., Lassmann H., Budka H., Grundke‐Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Wiche G., Seitelberger F., Wisniewski H. M., Acta Neuropathol. 1987, 74, 39. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

