Genetically driven brain serotonin deficiency facilitates panic-like escape behavior in mice
- PMID: 28972592
- PMCID: PMC5682603
- DOI: 10.1038/tp.2017.209
Genetically driven brain serotonin deficiency facilitates panic-like escape behavior in mice
Abstract
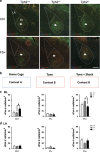
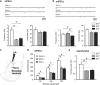
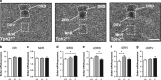
Multiple lines of evidence implicate brain serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine; 5-HT) system dysfunction in the pathophysiology of stressor-related and anxiety disorders. Here we investigate the influence of constitutively deficient 5-HT synthesis on stressor-related anxiety-like behaviors using Tryptophan hydroxylase 2 (Tph2) mutant mice. Functional assessment of c-Fos after associated foot shock, electrophysiological recordings of GABAergic synaptic transmission, differential expression of the Slc6a4 gene in serotonergic neurons were combined with locomotor and anxiety-like measurements in different contextual settings. Our findings indicate that constitutive Tph2 inactivation and consequential lack of 5-HT synthesis in Tph2 null mutant mice (Tph2-/-) results in increased freezing to associated foot shock and a differential c-Fos activity pattern in the basolateral complex of the amygdala. This is accompanied by altered GABAergic transmission as observed by recordings of inhibitory postsynaptic currents on principal neurons in the basolateral nucleus, which may explain increased fear associated with hyperlocomotion and escape-like responses in aversive inescapable contexts. In contrast, lifelong 5-HT deficiency as observed in Tph2 heterozygous mice (Tph+/-) is able to be compensated through reduced GABAergic transmission in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala based on Slc6a4 mRNA upregulation in subdivisions of dorsal raphe neurons. This results in increased activity of the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala due to associated foot shock. In conclusion, our results reflect characteristic syndromal dimensions of panic disorder and agoraphobia. Thus, constitutive lack of 5-HT synthesis influence the risk for anxiety- and stressor-related disorders including panic disorder and comorbid agoraphobia through the absence of GABAergic-dependent compensatory mechanisms in the basolateral nucleus of the amygdala.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Wittchen HU, Jacobi F, Rehm J, Gustavsson A, Svensson M, Jonsson B et al. The size and burden of mental disorders and other disorders of the brain in Europe 2010. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 2011; 21: 655–679. - PubMed
-
- Shekhar A, Sajdyk TS, Keim SR, Yoder KK, Sanders SK. Role of the basolateral amygdala in panic disorder. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1999; 877: 747–750. - PubMed
-
- Rauch SL, Shin LM, Wright CI. Neuroimaging studies of amygdala function in anxiety disorders. Ann NY Acad Sci 2003; 985: 389–410. - PubMed
-
- Naughton M, Mulrooney JB, Leonard BE. A review of the role of serotonin receptors in psychiatric disorders. Hum Psychopharmacol 2000; 15: 397–415. - PubMed
-
- Graeff FG, Guimaraes FS, De Andrade TG, Deakin JF. Role of 5-HT in stress, anxiety, and depression. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1996; 54: 129–141. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

