Metrics and Acquisition Modes for Fixation Stability as a Visual Function Biomarker
- PMID: 28973313
- PMCID: PMC6733530
- DOI: 10.1167/iovs.17-21710
Metrics and Acquisition Modes for Fixation Stability as a Visual Function Biomarker
Abstract
Purpose: To compare different metrics and acquisition modes of fixation stability as a new visual function biomarker in a large cohort of patients with ABCA4-related Stargardt disease from the multicenter prospective ProgStar study.
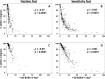
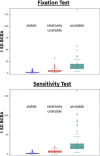
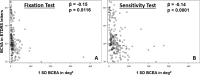
Methods: Fixation was tested during a separate fixation exam and also dynamically during a sensitivity exam, using fundus-tracking microperimetry (Nidek MP-1). Fixation data were analyzed using the bivariate contour ellipse area (BCEA), the 2/4 degree method, and the Fujii classification.
Results: In a total of 235 patients, the mean BCEA was larger when measured during the sensitivity exam (418 eyes; 12.5 vs. 4.6 deg2 during the fixation task in 427 eyes). Correlations between the two tests were generally weak. Fixation stability during the sensitivity test was significantly correlated with visual acuity. Comparing the BCEA values and the corresponding Fujii categories for these eyes revealed ranges of overlap where an eye with one defined BCEA value can fall into each of the three Fujii categories.
Conclusions: Patients may have limited ability to fixate over defined time periods, which leads to significant differences between shorter and longer measurements of fixation stability. The most appropriate way to use this functional biomarker appears to be using continuous metrics for fixation stability, such as the BCEA, during a macular sensitivity test.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Longitudinal Changes of Fixation Location and Stability Within 12 Months in Stargardt Disease: ProgStar Report No. 12.Am J Ophthalmol. 2018 Sep;193:54-61. doi: 10.1016/j.ajo.2018.06.003. Epub 2018 Jun 8. Am J Ophthalmol. 2018. PMID: 29890160 Free PMC article.
-
Macular Sensitivity Measured With Microperimetry in Stargardt Disease in the Progression of Atrophy Secondary to Stargardt Disease (ProgStar) Study: Report No. 7.JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017 Jul 1;135(7):696-703. doi: 10.1001/jamaophthalmol.2017.1162. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2017. PMID: 28542693 Free PMC article.
-
Factors Influencing Fixation Stability Area: A Comparison of Two Methods of Recording.Optom Vis Sci. 2018 Apr;95(4):384-390. doi: 10.1097/OPX.0000000000001201. Optom Vis Sci. 2018. PMID: 29554006
-
Microperimetry in Three Inherited Retinal Disorders.Semin Ophthalmol. 2019;34(4):334-339. doi: 10.1080/08820538.2019.1622025. Epub 2019 May 30. Semin Ophthalmol. 2019. PMID: 31146612 Review.
-
Fundus-driven perimetry (microperimetry) compared to conventional static automated perimetry: similarities, differences, and clinical applications.Can J Ophthalmol. 2013 Oct;48(5):358-63. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjo.2013.03.021. Epub 2013 Sep 2. Can J Ophthalmol. 2013. PMID: 24093180 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The vertical position of visual information conditions spatial memory performance in healthy aging.Commun Psychol. 2023 Jul 25;1(1):2. doi: 10.1038/s44271-023-00002-3. Commun Psychol. 2023. PMID: 39242667 Free PMC article.
-
The natural preferred retinal locus in patients with macular disease.Sci Rep. 2025 Jul 14;15(1):25348. doi: 10.1038/s41598-025-88421-6. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40659772 Free PMC article.
-
Alterations in Fixation Indices in Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma by Microperimetry.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 23;11(9):2368. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092368. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566493 Free PMC article.
-
The role of multimodal imaging and vision function testing in ABCA4-related retinopathies and their relevance to future therapeutic interventions.Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2021 Dec 19;13:25158414211056384. doi: 10.1177/25158414211056384. eCollection 2021 Jan-Dec. Ther Adv Ophthalmol. 2021. PMID: 34988368 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical Perspectives and Trends: Microperimetry as a Trial Endpoint in Retinal Disease.Ophthalmologica. 2021;244(5):418-450. doi: 10.1159/000515148. Epub 2021 Feb 10. Ophthalmologica. 2021. PMID: 33567434 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Walia S, Fishman GA. Natural history of phenotypic changes in Stargardt macular dystrophy. Ophthalmic Genet. 2009;30:63–68. - PubMed
-
- van Huet RA, Bax NM, Westeneng-van Haaften SC, et al. Foveal sparing in Stargardt disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2014;55:7467–7478. - PubMed
-
- Nakao T, Tsujikawa M, Sawa M, Gomi F, Nishida K. Foveal sparing in patients with Japanese Stargardt's disease and good visual acuity. Jpn J Ophthalmol. 2012;56:584–588. - PubMed
-
- Westeneng-van Haaften SC, Boon CJ, Cremers FP, Hoefsloot LH, den Hollander AI, Hoyng CB. Clinical and genetic characteristics of late-onset Stargardt's disease. Ophthalmology. 2012;119:1199–1210. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

