Structural insights of lincosamides targeting the ribosome of Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 28973455
- PMCID: PMC5622323
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkx658
Structural insights of lincosamides targeting the ribosome of Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
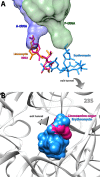
Antimicrobial resistance within a wide range of pathogenic bacteria is an increasingly serious threat to global public health. Among these pathogenic bacteria are the highly resistant, versatile and possibly aggressive bacteria, Staphylococcus aureus. Lincosamide antibiotics were proved to be effective against this pathogen. This small, albeit important group of antibiotics is mostly active against Gram-positive bacteria, but also used against selected Gram-negative anaerobes and protozoa. S. aureus resistance to lincosamides can be acquired by modifications and/or mutations in the rRNA and rProteins. Here, we present the crystal structures of the large ribosomal subunit of S. aureus in complex with the lincosamides lincomycin and RB02, a novel semisynthetic derivative and discuss the biochemical aspects of the in vitro potency of various lincosamides. These results allow better understanding of the drugs selectivity as well as the importance of the various chemical moieties of the drug for binding and inhibition.
© The Author(s) 2017. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures



References
-
- World Health Organization Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance. 2014; Geneva: World Health Organization.
-
- Lowy F.D. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N. Engl. J. Med. 1998; 339:520–532. - PubMed
-
- Marcinak J.F., Frank A.L.. Treatment of community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus in children. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2003; 16:265–269. - PubMed
-
- Johnson M.D., Decker C.F.. Antimicrobial agents in treatment of MRSA infections. Dis. Mon. 2008; 54:793–800. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

