Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View
- PMID: 28973479
- PMCID: PMC5629070
- DOI: 10.1210/er.2017-00073
Insulin Receptor Isoforms in Physiology and Disease: An Updated View
Abstract
The insulin receptor (IR) gene undergoes differential splicing that generates two IR isoforms, IR-A and IR-B. The physiological roles of IR isoforms are incompletely understood and appear to be determined by their different binding affinities for insulin-like growth factors (IGFs), particularly for IGF-2. Predominant roles of IR-A in prenatal growth and development and of IR-B in metabolic regulation are well established. However, emerging evidence indicates that the differential expression of IR isoforms may also help explain the diversification of insulin and IGF signaling and actions in various organs and tissues by involving not only different ligand-binding affinities but also different membrane partitioning and trafficking and possibly different abilities to interact with a variety of molecular partners. Of note, dysregulation of the IR-A/IR-B ratio is associated with insulin resistance, aging, and increased proliferative activity of normal and neoplastic tissues and appears to sustain detrimental effects. This review discusses novel information that has generated remarkable progress in our understanding of the physiology of IR isoforms and their role in disease. We also focus on novel IR ligands and modulators that should now be considered as an important strategy for better and safer treatment of diabetes and cancer and possibly other IR-related diseases.
Copyright © 2017 Endocrine Society.
Figures
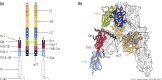






References
-
- Belfiore A, Frasca F, Pandini G, Sciacca L, Vigneri R. Insulin receptor isoforms and insulin receptor/insulin-like growth factor receptor hybrids in physiology and disease. Endocr Rev. 2009;30(6):586–623. - PubMed
-
- Pandini G, Frasca F, Mineo R, Sciacca L, Vigneri R, Belfiore A. Insulin/insulin-like growth factor I hybrid receptors have different biological characteristics depending on the insulin receptor isoform involved. J Biol Chem. 2002;277(42):39684–39695. - PubMed
-
- Menting JG, Whittaker J, Margetts MB, Whittaker LJ, Kong GK-W, Smith BJ, Watson CJ, Žáková L, Kletvíková E, Jiráček J, Chan SJ, Steiner DF, Dodson GG, Brzozowski AM, Weiss MA, Ward CW, Lawrence MC. How insulin engages its primary binding site on the insulin receptor. Nature. 2013;493(7431):241–245. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Menting JG, Lawrence CF, Kong GK-W, Margetts MB, Ward CW, Lawrence MC. Structural Congruency of Ligand Binding to the Insulin and Insulin/Type 1 Insulin-like Growth Factor Hybrid Receptors. Structure. 2015;23(7):1271–1282. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

