Surgical repair and reconstruction of aortic arch in debakey type I aortic dissection: recent advances and single-center experience in the application of branched stent graft
- PMID: 28974246
- PMCID: PMC5627456
- DOI: 10.1186/s13019-017-0649-6
Surgical repair and reconstruction of aortic arch in debakey type I aortic dissection: recent advances and single-center experience in the application of branched stent graft
Abstract
Background: Aortic dissection (AD) represents a clinically uncommon aortic pathology which predicts a dismal prognosis if not promptly treated. In acute Debakey type I AD (ADIAD), aortic lesion extends from aortic root to even distal abdominal aorta among which aortic arch and its three main branches still remain a great surgical challenge for repair and reconstruction. Several decades have witnessed the painstaking efforts of cardiovascular surgeons across the globe for optimizing the surgical procedures, from total or hemi-arch replacement, "elephant trunk" technique to branched stent graft. However, operative mortality and morbidity still remain to be reduced and surgical strategy is to be advanced and simplified, particularly the repair and reconstruction of aortic arch and supra-aortic vessels.
Methods: In this paper, we reviewed the relevant literature concerning recent advances in surgical intervention of aortic arch and summarized our opinions in the application of branched stent graft in ADIAD.
Results: The operative strategy for acute Debakey type I aortic dissection still remain to be advanced and simplified, especially the repair and reconstruction of aortic arch and supra-aortic vessels. For selection of branched stent grafts, the anatomic features and pathological changes of diseased arch are the crucial factors for clinical decision making.
Conclusions: Branched stent graft is potentially an effective alternative for the treatment of type I AD with diseased aortic arch and supra-aortic vessels. The selection of branched stent grafts still remains to be further discussed in large-scale studies in the future.
Keywords: Aortic arch; Aortic dissection; Branched stent graft.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Ethics approval for this study was obtained from the ethics review committee for human studies of School of Medicine, Shandong University.
Consent for publication
The patients included in the study provided their informed consent.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
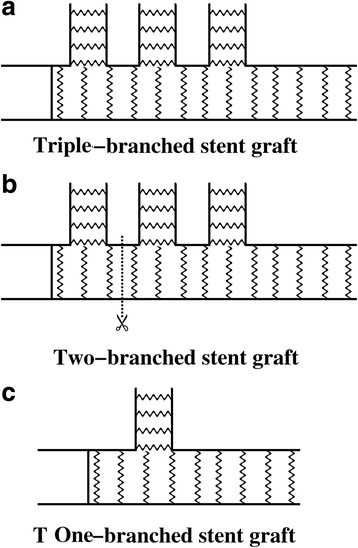
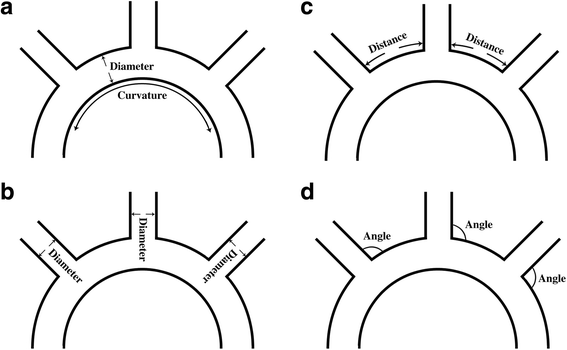
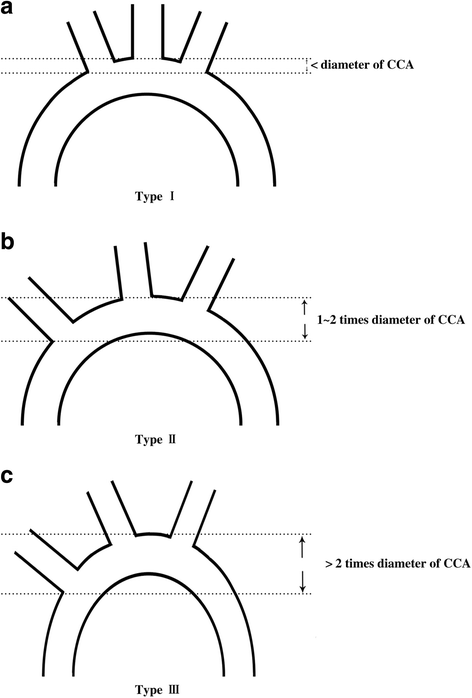
References
-
- Xiao ZY, Yao CL, Gu GR. Research update on the pathogenesis of aortic dissection. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2016;44(7):642–645. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

