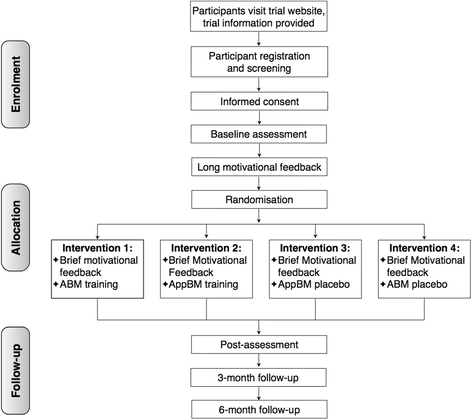
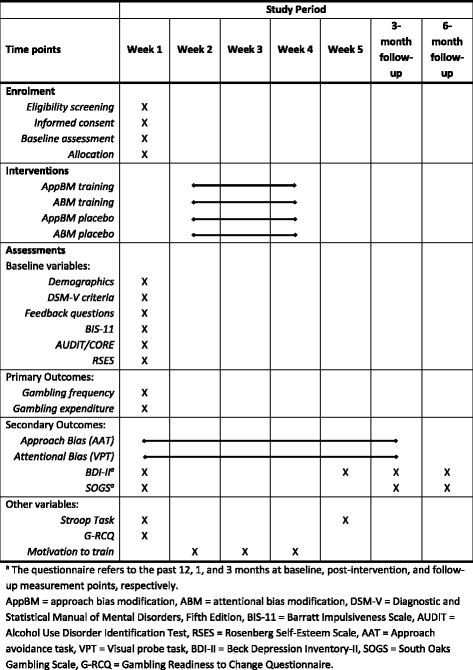
Effectiveness of two web-based cognitive bias modification interventions targeting approach and attentional bias in gambling problems: study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 28974265
- PMCID: PMC5627491
- DOI: 10.1186/s13063-017-2190-2
Effectiveness of two web-based cognitive bias modification interventions targeting approach and attentional bias in gambling problems: study protocol for a pilot randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Disordered gamblers have phenotypical and pathological similarities to those with substance use disorders (SUD), including exaggerated automatic cognitive processing of motivationally salient gambling cues in the environment (i.e., attentional and approach bias). Cognitive bias modification (CBM) is a family of computerised interventions that have proved effective in successfully re-training these automatic cognitive biases in SUD. CBM interventions can, in principle, be administered online, thus showing potential of being a low-cost, low-threshold addition to conventional treatments. This paper presents the design of a pilot randomised controlled trial exploring the effectiveness of two web-based CBM interventions targeting attentional and approach bias towards gambling cues in a sample of Dutch and Belgian problematic and pathological gamblers.
Methods/design: Participants (N = 182) are community-recruited adults experiencing gambling problems, who have gambled at least twice in the past 6 months and are motivated to change their gambling behaviour. After a baseline assessment session, participants are randomly assigned to one of four experimental conditions (attentional or approach bias training, or the placebo version of the two trainings) and complete six sessions of training. At baseline and before each training session, participants receive automated personalised feedback on their gambling motives and reasons to quit or reduce gambling. The post-intervention, 1-month, and 3-month follow-up assessments will examine changes in gambling behaviour, with frequency and expenditure as primary outcomes, and depressive symptoms and gambling-related attentional and approach biases as secondary outcomes. Secondary analyses will explore possible moderators (interference control capacity and trait impulsivity) and mediators (change in cognitive bias) of training effects on the primary outcomes.
Discussion: This study is the first to explore the effectiveness of an online CBM intervention for gambling problems. The results of this study can be extremely valuable for developing e-health interventions for gambling problems and further understanding the role of motivational implicit cognitive processes underlying problematic gambling behaviour.
Trial registration: Netherlands Trial Register, NTR5096 . Registered on 11 March 2015.
Keywords: Addiction; Approach bias; Attentional bias; Cognitive bias modification; Gambling; Randomised controlled trial; e-health.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol (version 1.3 dated 15-07-2014) has been approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of the University of Antwerp (October 2014, Belgian registration number: B300201422158) and by the Ethics Committee of the University of Amsterdam (August 2014, Protocol number: 2014-DP-3774). Upon registration on the study online platform, participants must read the information page and provide digital informed consent in order to participate in the study.
Consent for publication
The results of this study will be presented to the public and the scientific community through publications in scientific journals and presentations at conferences. Participants are fully informed that the results of the study will be published in anonymised format and are further asked to give their permission to do so in the digital informed consent form.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
How We Lost 90% of Participants on a Bad Bet: Results from a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial on Cognitive Bias Modification in Problem Gamblers.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Jun;40(2):521-554. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10263-6. Epub 2023 Nov 25. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 38006537 Clinical Trial.
-
Combining cognitive bias modification training with motivational support in alcohol dependent outpatients: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.Trials. 2015 Feb 26;16:63. doi: 10.1186/s13063-015-0576-6. Trials. 2015. PMID: 25888158 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Luck, come here! Automatic approach tendencies toward gambling cues in moderate- to high-risk gamblers.Addiction. 2018 Feb;113(2):289-298. doi: 10.1111/add.14071. Epub 2017 Nov 27. Addiction. 2018. PMID: 29055971
-
The effectiveness of attentional bias modification for substance use disorder symptoms in adults: a systematic review.Syst Rev. 2018 Oct 13;7(1):160. doi: 10.1186/s13643-018-0822-6. Syst Rev. 2018. PMID: 30316302 Free PMC article.
-
From sign-tracking to attentional bias: Implications for gambling and substance use disorders.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020 Apr 20;99:109861. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2020.109861. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2020. PMID: 31931091 Review.
Cited by
-
A Systematic Review of Attentional Bias in Problem Gambling.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Jun;40(2):493-519. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10260-9. Epub 2023 Nov 9. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 37943393 Free PMC article.
-
The specificity of attentional biases by type of gambling: An eye-tracking study.PLoS One. 2018 Jan 31;13(1):e0190614. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0190614. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29385164 Free PMC article.
-
Impulsivity, Emotion Regulation, Cognitive Distortions and Attentional Bias in a Spanish Sample of Gambling Disorder Patients: Comparison between Online and Land-Based Gambling.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 May 3;18(9):4869. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18094869. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34063619 Free PMC article.
-
A Scoping Review of Cognitive Bias in Internet Addiction and Internet Gaming Disorders.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Jan 6;17(1):373. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17010373. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 31935915 Free PMC article.
-
How We Lost 90% of Participants on a Bad Bet: Results from a Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial on Cognitive Bias Modification in Problem Gamblers.J Gambl Stud. 2024 Jun;40(2):521-554. doi: 10.1007/s10899-023-10263-6. Epub 2023 Nov 25. J Gambl Stud. 2024. PMID: 38006537 Clinical Trial.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (DSM-5®). American Psychiatric Pub; 2013.
-
- Petry N. Comorbidity of disordered gambling and other psychiatric disorders. In: Petry N, editor. Pathological gambling: etiology, comorbidity and treatment. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association; 2005. pp. 85–115.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous