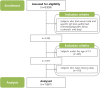
Serum Zinc Status and Its Association with Allergic Sensitization: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- PMID: 28974756
- PMCID: PMC5626772
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-017-13068-x
Serum Zinc Status and Its Association with Allergic Sensitization: The Fifth Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
Abstract
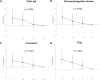
Zinc (Zn) is an essential trace element that plays important roles in the immune system. There is little known about the role of trace elements in allergic diseases, and previous reports have shown conflicting results. The aim of this study was to investigate the relationship between serum Zn levels and total or allergen-specific immunoglobulin E (IgE) levels. The initial candidates for this study were those who participated in the 5th Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2010 (n = 8,958), and 1,867 adults who had serum total and allergen specific-IgE levels measured were included. Upon adjusting for covariates, mean total IgE, Dermatophagoides farinae and dog-specific IgE levels increased significantly as the Zn levels decrease from the highest to the lowest quartile (p = 0.009, 0.004, and < 0.001, respectively). The multiple logistic regression analyses showed significant negative linear correlations between serum Zn levels and total, D. farinae-, cockroach-, and dog-specific IgE levels (p-value for linear trend = 0.004, 0.006, 0.027, and < 0.001, respectively). This study demonstrated that total/allergen specific IgE and Zn levels are significantly inversely related.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Shankar AH, Prasad AS. Zinc and immune function: the biological basis of altered resistance to infection. The American journal of clinical nutrition. 1998;68:447s–463s. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical