Influence of Apolipoprotein E on the Lipid Profile and Postprandial Triglyceride Levels in Brazilian Postmenopausal Women With Artery Disease
- PMID: 28974920
- PMCID: PMC5613840
- DOI: 10.1177/1179546817731110
Influence of Apolipoprotein E on the Lipid Profile and Postprandial Triglyceride Levels in Brazilian Postmenopausal Women With Artery Disease
Abstract
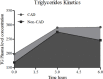
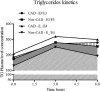
This study confirms the association of risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) and the apoE polymorphisms, specifically related to the APOE*4 allele, with coronary disease in postmenopausal women. Significantly altered values of the lipid profile were found in patients when compared with controls, independent of the presence of the APOE*4 allele. However, the controls showed higher high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) levels and reduced triglyceride (TG) levels, differing significantly from patients. In this case, the study of subgroups, considering the APOE*3/3 and APOE*3/4 genotypes, suggests that the APOE*4 allele is not implicated in the variations of the lipid profile of patients and determined an increase in the production levels of HDL-C and a reduction in TG highly benefiting the control group compared with APOE*3/3 genotype. The metabolic kinetics of TG, although with the same pattern between groups, and the presence of the APOE*4 allele are suggested to be associated with accelerated clearance compared with APOE*3 allele in non-CAD group.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; apolipoprotein E; cholesterol; postmenopause; postprandial triglycerides.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Conflicting Interests:The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The presence of apolipoprotein epsilon4 and epsilon2 alleles augments the risk of coronary artery disease in type 2 diabetic patients.Clin Biochem. 2007 Oct;40(15):1150-6. doi: 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2007.06.010. Epub 2007 Jul 6. Clin Biochem. 2007. PMID: 17689519
-
Apolipoproteins B and E, and angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) genetic polymorphisms in Italian women with coronary artery disease (CAD) and their relationships with plasma lipid and apolipoprotein levels.Clin Genet. 1997 Aug;52(2):77-82. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-0004.1997.tb02522.x. Clin Genet. 1997. PMID: 9298741
-
Role of lipid, apolipoprotein levels and apolipoprotein E genotype in young Italian patients with myocardial infarction.Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 1999 Jun;9(3):118-24. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 1999. PMID: 10464784
-
Relevance of apolipoprotein E4 for the lipid profile of Brazilian patients with coronary artery disease.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007 Feb;40(2):189-97. doi: 10.1590/s0100-879x2007000200005. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2007. PMID: 17273655
-
Triglyceride as a risk factor for coronary artery disease.Am J Cardiol. 1998 Nov 5;82(9A):22Q-25Q. doi: 10.1016/s0002-9149(98)00770-x. Am J Cardiol. 1998. PMID: 9819100 Review.
Cited by
-
Multi-Omics Analysis to Generate Hypotheses for Mild Health Problems in Monkeys.Metabolites. 2021 Oct 13;11(10):701. doi: 10.3390/metabo11100701. Metabolites. 2021. PMID: 34677416 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guang-da X, You-ying L, Zhi-song C, Yu-sheng H, Xiang-jiu Y. Apolipoprotein e4 allele is predictor of coronary artery disease death in elderly patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Atherosclerosis. 2004;175:77–81. - PubMed
-
- Castelli WP. Epidemiology of coronary heart disease: the Framingham study. Am J Med. 1984;76:4–12. - PubMed
-
- Tsang TS, Barnes ME, Gersh BJ, Hayes SN. Risks of coronary heart disease in women: current understanding and evolving concepts. Mayo Clin Proc. 2000;75:1289–1303. - PubMed
-
- Camsari A, Tamer L, Aras Ates N, et al. Apolipoprotein E polymorphism in diabetic and non-diabetic patients: does it really contribute to atherosclerosis? Acta Cardiol. 2005;60:409–414. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

