Sustained remission in rheumatoid arthritis: latest evidence and clinical considerations
- PMID: 28974987
- PMCID: PMC5613855
- DOI: 10.1177/1759720X17720366
Sustained remission in rheumatoid arthritis: latest evidence and clinical considerations
Abstract
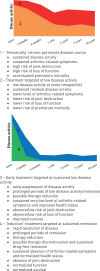
Sustained remission is an ultimate treatment goal in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA). Historically the frequency of sustained remission was low but the frequency of achieved sustained remission is increasing over time. The last years' clinical studies of tight control targeted treatment and intervention trials of early use of intensive strategy suggest that these treatment strategies are associated with higher rates of sustained remission. Achievement of sustained remission, in particular but not limited to early sustained remission, can provide tapering and stopping disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs). With new treatment strategies drug-free sustained remission is becoming an achievable goal. Sustained remission is associated with improved outcomes in regard to function, patient-reported outcomes and survival. Drug-free sustained remission is characterized by normalized function ability and survival. Sustained remission and, in particular, drug-free sustained remission offer hope that early identification of patients with arthritis, early improved novel treatments and treatment with target to achieve remission may potentially transform the progressive course of RA disease and disrupt RA chronicity. In this review we summarize the recent evidence on sustained remission in patients with RA, treatment strategies to achieve sustained remission, management of patients in sustained remission and significance of sustained remission from the patient perspective.
Keywords: disability; drug-free remission; outcome; rheumatoid arthritis; sustained remission; treatment strategy.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: Tom Huizinga and the Department of Rheumatology, Leiden University Medical Center, has received lecture fees/consultancy fees from Merck, UCB, Bristol Myers Squibb, Biotest AG, Janssen, Pfizer, GSK, Novartis, Roche, Sanofi-Aventis, Abbott, Crescendo Bioscience, Nycomed, Boeringher, Takeda, Zydus, Epirus and Eli Lilly.
Figures
References
-
- Combe B, Landewe R, Daien CI, et al. 2016 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of early arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 2016; 76: 948–959. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical