Quantification of pulmonary regurgitation in patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot by 2D phase-contrast MRI: Differences between the standard method of velocity averaging and a pixel-wise analysis
- PMID: 28975024
- PMCID: PMC5613799
- DOI: 10.1177/2048004017731986
Quantification of pulmonary regurgitation in patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot by 2D phase-contrast MRI: Differences between the standard method of velocity averaging and a pixel-wise analysis
Abstract
Objectives: To compare the values of pulmonary regurgitation in patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot quantified from two-dimensional phase-contrast data, by using a new pixel-wise analysis and the standard velocity-averaging method.
Design: Quantitative in silico and in vivo analysis.
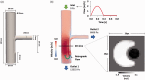
Setting: Hospital Sótero del Río. The magnetic resonance images were acquired using a Philips Achieva 1.5T scanner.
Participants: Twenty-five patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot who underwent cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging requested by their referring physicians were included in this study.
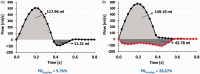
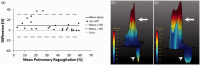
Main outcome measures: Using a computational fluid dynamics simulation, we validated our pixel-wise method, quantifying the error of our method in comparison with the standard method. The patients underwent a standard two-dimensional phase-contrast magnetic resonance imaging acquisition for quantifying pulmonary artery flow. Pulmonary regurgitation fraction was estimated by using our pixel-wise and the standard method. The two-dimensional flow profiles were inspected looking for simultaneous antegrade and retrograde flows in the same cardiac phase. Statistical analysis was performed with t-test for related samples, Bland-Altman plots, and Pearson correlation coefficient.
Results: Estimation of pulmonary regurgitation fraction using the pixel-wise analysis revealed higher values compared with the standard method (39 ± 16% vs. 30 ± 22%, p-value <0.01). Eight patients (32%) had a difference of more than 10% between methods. Analysis of two-dimensional flow profiles in these patients revealed simultaneous antegrade and retrograde flows through the pulmonary artery during systole-early diastole.
Conclusion: Quantification of pulmonary regurgitation fraction in patients with repaired Tetralogy of Fallot through a pixel-wise analysis yields higher values of pulmonary regurgitation compared with the standard velocity-averaging method.
Keywords: Tetralogy of Fallot; magnetic resonance imaging; pulmonary valve insufficiency; two-dimensional flow.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Pixel-wise derivation of pulmonary regurgitation index could influence clinical decision: A phase-contrast MR imaging study on patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot.Eur J Radiol. 2017 Aug;93:46-51. doi: 10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.05.027. Epub 2017 May 25. Eur J Radiol. 2017. PMID: 28668430
-
Ventricular kinetic energy may provide a novel noninvasive way to assess ventricular performance in patients with repaired tetralogy of Fallot.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015 May;149(5):1339-47. doi: 10.1016/j.jtcvs.2014.11.085. Epub 2014 Dec 4. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2015. PMID: 25623907 Free PMC article.
-
Right ventricular diastolic function in children with pulmonary regurgitation after repair of tetralogy of Fallot: volumetric evaluation by magnetic resonance velocity mapping.J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996 Dec;28(7):1827-35. doi: 10.1016/S0735-1097(96)00387-7. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1996. PMID: 8962573
-
Pulmonary valve replacement after operative repair of tetralogy of Fallot: meta-analysis and meta-regression of 3,118 patients from 48 studies.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013 Dec 10;62(23):2227-43. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2013.04.107. Epub 2013 Sep 28. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 24080109
-
Clinical applications of cardiac magnetic resonance imaging after repair of tetralogy of Fallot.Pediatr Cardiol. 2000 Jan-Feb;21(1):70-9. doi: 10.1007/s002469910009. Pediatr Cardiol. 2000. PMID: 10672616 Review.
Cited by
-
Fully Three-Dimensional Hemodynamic Characterization of Altered Blood Flow in Bicuspid Aortic Valve Patients With Respect to Aortic Dilatation: A Finite Element Approach.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 May 18;9:885338. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.885338. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 35665243 Free PMC article.
-
Highly accelerated, real-time phase-contrast MRI using radial k-space sampling and GROG-GRASP reconstruction: a feasibility study in pediatric patients with congenital heart disease.NMR Biomed. 2020 May;33(5):e4240. doi: 10.1002/nbm.4240. Epub 2020 Jan 24. NMR Biomed. 2020. PMID: 31977117 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning based automated left atrial segmentation and flow quantification of real time phase contrast MRI in patients with atrial fibrillation.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025 Jun;41(6):1197-1208. doi: 10.1007/s10554-025-03407-9. Epub 2025 Apr 29. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2025. PMID: 40301204 Free PMC article.
-
Four-dimensional flow cardiovascular magnetic resonance in tetralogy of Fallot: a systematic review.J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021 May 20;23(1):59. doi: 10.1186/s12968-021-00745-0. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson. 2021. PMID: 34011372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Apitz C Webb GD andRedington AN.. Tetralogy of Fallot. Lancet 2009; 374: 1462–1471. - PubMed
-
- Ho KW, Tan RS, Wong KY, et al. Late complications following Tetralogy of Fallot repair: the need for long-term follow-up. Ann Acad Med Singapore 2007; 36: 947–953. - PubMed
-
- Bouzas B Kilner PJ andGatzoulis MA.. Pulmonary regurgitation: not a benign lesion. Eur Heart J 2005; 26: 433–439. - PubMed
-
- Voser EM Kellenberger CJ andValsangiacomo Buechel ER.. Effect of pulmonary regurgitation on distensibility and flow of the branch pulmonary arteries in Tetralogy of Fallot. Pediatr Cardiol 2013; 34: 1118–1124 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

