Characterizing Orthostatic Tremor Using a Smartphone Application
- PMID: 28975048
- PMCID: PMC5623759
- DOI: 10.7916/D8V12GRJ
Characterizing Orthostatic Tremor Using a Smartphone Application
Abstract
Background: Orthostatic tremor is one of the few tremor conditions requiring an electromyogram for definitive diagnosis since leg tremor might not be visible to the naked eye.
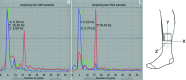
Phenomenology shown: An iOS application (iSeismometer, ObjectGraph LLC, New York) using an Apple iPhone 5 (Cupertino, CA, USA) inserted into the patient's sock detected a tremor with a frequency of 16.4 Hz on both legs.
Educational value: The rapid and straightforward accelerometer-based recordings accomplished in this patient demonstrate the ease with which quantitative analysis of orthostatic tremor can be conducted and, importantly, demonstrates the potential application of this approach in the assessment of any lower limb tremor.
Keywords: Accelerometer; diagnosis; orthostatic tremor; smartphone; wearable.
Conflict of interest statement
Funding: None. Conflict of Interest: The authors report no conflict of interest. Ethics Statement: All patients that appear on video have provided written informed consent; authorization for the videotaping and for publication of the videotape was provided.
Figures
References
-
- McManis PG, Sharbrough FW. Orthostatic tremor: clinical and electrophysiologic characteristics. Muscle Nerve. 1993;16:1254–1260. doi: 10.1002/mus.880161117. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Brown P. New clinical sign for orthostatic tremor. Lancet. 1995;346:306–307. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(95)92190-7. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Araújo R, Tábuas-Pereira M, Almendra L, Ribeiro J, Arenga M, Negrão L, et al. Tremor frequency assessment by iPhone® applications: correlation with EMG analysis. J Parkinson’s Dis. 2016;6:717–721. doi: 10.3233/JPD-160936. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical