PET Molecular Imaging Research of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 28975571
- PMCID: PMC5626800
- DOI: 10.1007/s11910-017-0794-2
PET Molecular Imaging Research of Levodopa-Induced Dyskinesias in Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
Purpose of review: To review the current status of positron emission tomography (PET) molecular imaging research of levodopa-induced dyskinesias (LIDs) in Parkinson's disease (PD).
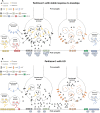
Recent findings: Recent PET studies have provided robust evidence that LIDs in PD are associated with elevated and fluctuating striatal dopamine synaptic levels, which is a consequence of the imbalance between dopaminergic and serotonergic terminals, with the latter playing a key role in mishandling presynaptic dopamine release. Long-term exposure to levodopa is no longer believed to solely induce LIDs, as studies have highlighted that PD patients who go on to develop LIDs exhibit elevated putaminal dopamine release before the initiation of levodopa treatment, suggesting the involvement of other mechanisms, including altered neuronal firing and abnormal levels of phosphodiesterase 10A. Dopaminergic, serotonergic, glutamatergic, adenosinergic and opioid systems and phosphodiesterase 10A levels have been shown to be implicated in the development of LIDs in PD. However, no system may be considered sufficient on its own for the development of LIDs, and the mechanisms underlying LIDs in PD may have a multisystem origin. In line with this notion, future studies should use multimodal PET molecular imaging in the same individuals to shed further light on the different mechanisms underlying the development of LIDs in PD.
Keywords: Dyskinesias; Molecular imaging; Parkinson’s disease; Positron emission tomography.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Funding
This study was not funded.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The serotonergic system in Parkinson's patients with dyskinesia: evidence from imaging studies.J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018 Aug;125(8):1217-1223. doi: 10.1007/s00702-017-1823-7. Epub 2017 Dec 20. J Neural Transm (Vienna). 2018. PMID: 29264660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular imaging of levodopa-induced dyskinesias.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015 Jun;72(11):2107-17. doi: 10.1007/s00018-015-1854-x. Epub 2015 Feb 15. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2015. PMID: 25681866 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Serotonergic mechanisms responsible for levodopa-induced dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease patients.J Clin Invest. 2014 Mar;124(3):1340-9. doi: 10.1172/JCI71640. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Clin Invest. 2014. PMID: 24531549 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: views from positron emission tomography studies.Eur J Neurol. 2014 May;21(5):694-9, e39-43. doi: 10.1111/ene.12362. Epub 2014 Jan 28. Eur J Neurol. 2014. PMID: 24471508 Review.
-
The role of pallidal serotonergic function in Parkinson's disease dyskinesias: a positron emission tomography study.Neurobiol Aging. 2015 Apr;36(4):1736-1742. doi: 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2014.12.037. Epub 2015 Jan 6. Neurobiol Aging. 2015. PMID: 25649022
Cited by
-
Neuroimaging of Sleep Disturbances in Movement Disorders.Front Neurol. 2018 Sep 11;9:767. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00767. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 30323786 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Graph Theory on Brain Cortical Sources in Parkinson's Disease: The Analysis of 'Small World' Organization from EEG.Sensors (Basel). 2021 Oct 31;21(21):7266. doi: 10.3390/s21217266. Sensors (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34770573 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic administration of the histamine H3 receptor agonist immepip decreases L-Dopa-induced dyskinesias in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jun;236(6):1937-1948. doi: 10.1007/s00213-019-5182-y. Epub 2019 Feb 14. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30762089
-
Repetitive Levodopa Treatment Drives Cell Type-Specific Striatal Adaptations Associated With Progressive Dyskinesia in Parkinsonian Mice.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2025 May 21:2025.05.16.654598. doi: 10.1101/2025.05.16.654598. bioRxiv. 2025. PMID: 40475531 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Serotonin-Related Functional Genetic Variants Affect the Occurrence of Psychiatric and Motor Adverse Events of Dopaminergic Treatment in Parkinson's Disease: A Retrospective Cohort Study.J Pers Med. 2022 Feb 11;12(2):266. doi: 10.3390/jpm12020266. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 35207756 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Birkmayer W, Hornykiewicz O. The effect of l-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine (= DOPA) on akinesia in parkinsonism 1961. Wien Klin Wochenschr. 2001;113(22):851–4. - PubMed
-
- Niccolini F, Loane C, Politis M. Dyskinesias in Parkinson's disease: views from positron emission tomography studies. Eur J Neurol. 2014;21(5):694-9, e39-43. 10.1111/ene.12362. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

