Propensity score matching analysis of the impact of Syntax score and Syntax score II on new onset atrial fibrillation development in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
- PMID: 28975725
- PMCID: PMC6931703
- DOI: 10.1111/anec.12504
Propensity score matching analysis of the impact of Syntax score and Syntax score II on new onset atrial fibrillation development in patients with ST segment elevation myocardial infarction
Abstract
Background: New-onset atrial fibrillation (NOAF) is a common complication in the setting of ST segment elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI), and worsened short/long-term prognosis. Several clinical parameters have already been associated with NOAF development. However, relationship between NOAF and coronary artery disease (CAD) severity in STEMI patients is unclear. This study evaluates the relationship between NOAF and CAD severity using Syntax score (SS) and Syntax score II (SSII) in STEMI patients who were treated with primary percutaneous coronary intervention (pPCI).
Method: We enrolled 1,565 consecutive STEMI patients who were treated with pPCI. Patients with NOAF were compared to patients without NOAF in the entire study population and in a matched population defined by propensity score matching.
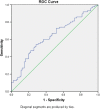
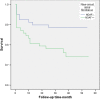
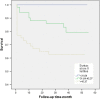
Results: Patients with NOAF had significantly higher SS and SSII than those without, both in the matched population (18.6 ± 4 vs 16.75 ± 3.6; p < .001 and 42 ± 13.4 vs 35.1 ± 13.1; p < .001, respectively), and in all study population (18.6 ± 4 vs 16.5 ± 4.6; p < .001 and 42 ± 13.3 vs 31.5 ± 11.9; p < .001 respectively). SSII, compared to its components, was the only independent predictor of NOAF (OR: 1,041 95% CI: 1.015-1.068; p = .002). In the long-term follow-up, all-cause long-term mortality was significantly higher in patients with NOAF than those without NOAF (23.3% vs. 11%; p = .032).
Conclusion: This is the first study to comprehensively examine the relationship between NOAF development and CAD severity using SS and SSII. We demonstrated that, in STEMI patients, high SSII was significantly related to NOAF and was an independent predictor of NOAF. Furthermore, patients with NOAF were associated with poor prognosis.
Keywords: ST elevation myocardial infarction; SYNTAX score; SYNTAX score II; atrial fibrillation.
© 2017 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Value of Syntax Score II in Prediction of New-Onset Atrial Fibrillation in Patients With NSTE-ACS Undergoing Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.Angiology. 2019 Oct;70(9):860-866. doi: 10.1177/0003319719854242. Epub 2019 Jun 6. Angiology. 2019. PMID: 31170823
-
Long term prognosis of atrial fibrillation in ST-elevation myocardial infarction patients undergoing percutaneous coronary intervention.Int J Cardiol. 2017 Aug 1;240:228-233. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.03.060. Epub 2017 Mar 16. Int J Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28390742
-
Association of the SYNTAX Score II with cardiac rupture in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction undergoing a primary percutaneous coronary intervention.Coron Artery Dis. 2018 Mar;29(2):97-103. doi: 10.1097/MCA.0000000000000571. Coron Artery Dis. 2018. PMID: 29028739
-
New-onset atrial fibrillation and outcomes following isolated coronary artery bypass surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Cardiol. 2020 Sep;43(9):928-934. doi: 10.1002/clc.23414. Epub 2020 Jul 21. Clin Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32696468 Free PMC article.
-
Atrial fibrillation in acute ST-elevation myocardial infarction: clinical and prognostic features.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2012 Nov;8(4):281-9. doi: 10.2174/157340312803760857. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2012. PMID: 22920476 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The interaction between neutrophils and atrial myocytes in the occurrence and development of atrial fibrillation.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):519. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04193-3. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39333891 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of potential biomarkers for atrial fibrillation and stable coronary artery disease based on WGCNA and machine algorithms.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Aug 2;24(1):401. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04062-z. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39090590 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of platelet-to-albumin ratio combined with the C2HEST score for New-Onset atrial fibrillation in elderly patients with acute ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):521. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04200-7. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39333846 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Lesion Complexity and the CHA2DS2-VASc Score on Spontaneous Reperfusion in Patients with ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Int J Clin Pract. 2022 Feb 9;2022:8066780. doi: 10.1155/2022/8066780. eCollection 2022. Int J Clin Pract. 2022. PMID: 35685511 Free PMC article.
-
The value of syntax score to predict new-onset atrial fibrillation in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019 Jul;24(4):e12622. doi: 10.1111/anec.12622. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Ann Noninvasive Electrocardiol. 2019. PMID: 30615236 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Al‐Thani, H. A. , El‐Menyar, A. , Zubaid, M. , Rashed, W. A. , Ridha, M. , Almahmeed, W. , … Al Suwaidi, J. (2011). Peripheral arterial disease in patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome in six middle eastern countries. International Journal of Vascular Medicine, 2011, 815902. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Camm, A. J. , Kirchhof, P. , Lip, G. Y. , Schotten, U. , Savelieva, I. , Ernst, S. , … Rutten, F. H. (2010). European Heart Rhythm Association, European Association for Cardio‐Thoracic Surgery, Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation: The Task Force for the Management of Atrial Fibrillation of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). European Heart Journal, 31, 2369–2429. - PubMed
-
- Coumel, P. (1996). Autonomic influences in atrial tachyarrhythmias. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 7(10), 999–1007. - PubMed
-
- Crenshaw, B. S. , Ward, S. R. , Granger, C. B. , Stebbins, A. L. , Topol, E. J. , & Califf, R. M. (1997). Atrial fibrillation in the setting of acute myocardial infarction: The GUSTO‐I experience. Global Utilization of Streptokinase and TPA for Occluded Coronary Arteries. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 30, 406–413. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

