Cyclosporine and Vancomycin + Amikacin Induced Hot Kidney Appearance in a Young Adult and a Pediatric Patient
- PMID: 28976336
- PMCID: PMC5643941
- DOI: 10.4274/mirt.30592
Cyclosporine and Vancomycin + Amikacin Induced Hot Kidney Appearance in a Young Adult and a Pediatric Patient
Abstract
The appearance of a hot kidney on bone scintigraphy is rare and can be seen due to various factors. In our clinic, we observed hot kidney appearance in two patients to whom technetium-99m methylene diphosphonate (Tc-99m MDP) whole body scan has been performed: a young male adult at the age of 18 who was diagnosed with acute lymphocytic leukemia with a presumptive diagnosis of avascular necrosis, and a 9-year-old girl with cystitis for a pre-diagnosis of osteomyelitis. The first patient had a history of cyclosporine usage and the second patient was being treated with amikacin + vancomycin. To the best of our knowledge, we present the first cases where hot-kidney appearance on Tc-99m MDP whole body scan due to the use of cyclosporin and amikacin + vancomycin is demonstrated.
Kemik sintigrafisinde hot kidney görünümü nadir olup, çeşitli faktörlere bağlı olarak görülebilmektedir. Kliniğimizde teknesyum-99m metilen difosfanat (Tc-99m MDP) tüm vücut kemik sintigrafisi yaptığımız iki hastada; ilki avasküler nekroz ön tanısı ile 18 yaşında akut lenfositer lösemi tanılı genç erişkin erkekte, diğeri osteomiyelit ön tanısı ile 9 yaşında sistit tanılı kız çocuğunda hot kidney görünümü izledik. İlk hastada siklosporin kullanım öyküsü vardı, ikinci hasta ise amikasin + vankomisin tedavisi altındaydı. Bildiğimiz kadarıyla, Tc-99m MDP tüm vücut kemik sintigrafisinde siklosporin ve amikasin + vankomisin kullanımına bağlı hot kidney görünümünün gösterildiği ilk olguları sunuyoruz. Anahtar kelimeler: Böbrek, Tc-99m medronat, radyonüklid görüntüleme.
Keywords: Kidney; Tc-99m medronate radionuclide imaging..
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
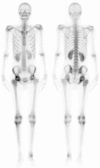
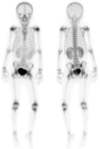
Similar articles
-
Comparison of Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate, Tc-99m human immune globulin, and Tc-99m-labeled white blood cell scintigraphy in the diabetic foot.Clin Nucl Med. 2001 Dec;26(12):1016-21. doi: 10.1097/00003072-200112000-00005. Clin Nucl Med. 2001. PMID: 11711704
-
Different findings in Tc-99m MDP bone scintigraphy of patients with sickle cell disease: report of three cases.Ann Nucl Med. 2007 Jul;21(5):311-4. doi: 10.1007/s12149-007-0025-z. Epub 2007 Jul 25. Ann Nucl Med. 2007. PMID: 17634851
-
The diagnostic value of (99m)Tc-IgG scintigraphy in the diabetic foot and comparison with (99m)Tc-MDP scintigraphy.J Nucl Med Technol. 2011 Sep;39(3):226-30. doi: 10.2967/jnmt.110.085498. Epub 2011 Jul 27. J Nucl Med Technol. 2011. PMID: 21795373
-
Chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis demonstrated by Tc-99m methylene diphosphonate bone scan.Clin Nucl Med. 2008 Jan;33(1):61-3. doi: 10.1097/RLU.0b013e31815c5035. Clin Nucl Med. 2008. PMID: 18097265
-
A report on the incidence of intestinal 99mTc-methylene diphosphonate uptake of bone scans and a review of the literature.Nucl Med Commun. 2006 Nov;27(11):877-85. doi: 10.1097/01.mnm.0000237991.44948.13. Nucl Med Commun. 2006. PMID: 17021428 Review.
References
-
- Langsteger W, Rezaee A, Pirich C, Beheshti M. 18F-NaF-PET/CT and 99mTc MDP Bone Scintigraphy in the Detection of Bone Metastases in Prostate Cancer. Semin Nucl Med. 2016;46:491–501. - PubMed
-
- Koizumi K, Tonami N, Hisada K. Diffusely increased Tc-99m-MDP uptake in both kidneys. Clin Nucl Med. 1981;6:362–365. - PubMed
-
- Ting A, Freund J. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory-induced acute renal failure detected on bone scintigraphy. Clin Nucl Med. 2004;29:318–319. - PubMed
-
- Gentili A, Miron SD, Adler LP, Bellon EM. Incidental detection of urinary tract abnormalities with skeletal scintigraphy. Radiographics. 1991;11:571–579. - PubMed
-
- Choy D, Murray IP, Hoschl R. The effect of iron on the biodistribution of bone scanning agents in humans. Radiology. 1981;140:197–202. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
